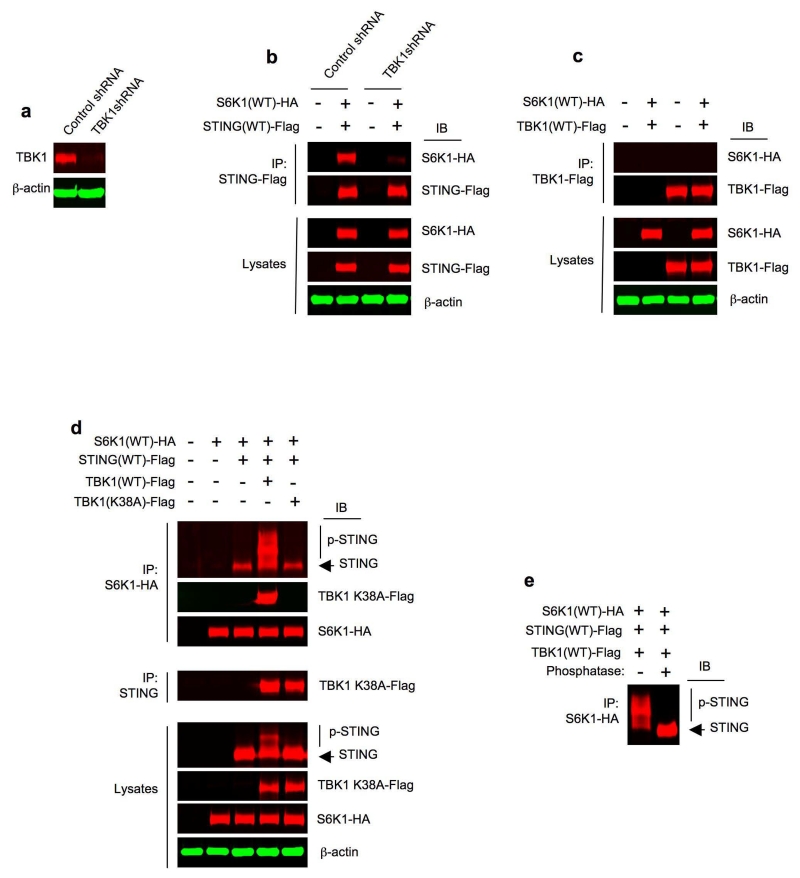
Figure 7.
S6K1 interacts with STING and TBK1 to form a tripartite complex. (a) Immunoblot analysis of TBK1 in control shRNA or TBK1 shRNA HEK293T cells. β-actin as loading control. (b) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis of the interaction between S6K1(WT)-HA and STING(WT)-Flag in control shRNA or TBK1 shRNA HEK293T cells. Lysates (below), immunoblot analysis of S6K1-HA, STING-Flag and β-actin as loading control. (c) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis of the interaction between S6K1(WT)-HA and TBK1(WT)-Flag in HEK293T cells transfected with respective plasmids. Lysates (below), immunoblot analysis of S6K1-HA, TBK1-Flag and β-actin as loading control. (d) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis of the interaction between S6K1(WT)-HA, STING(WT)-Flag, TBK1(WT)-Flag or TBK1(K38A)-Flag in HEK293T cells transfected with respective plasmids for 24 h. Lysates (below), immunoblot analysis of STING, S6K1-HA, TBK1-Flag and β-actin as loading control. (e) Immunoblot analysis of STING in the immunoprecipitates pulled down by anti-S6K1-HA from the whole cell lysates of HEK293T cells triply transfected with S6K1(WT)-HA, STING(WT)-Flag and TBK1(WT)-Flag for 24 h, treated with (+) or without (−) calf intestine phosphatase. Data are representative of four independent experiments (a-e).