Figure 1. Combined heterozygous reduction in Pdx1 and Oc1 gene dosage has a broad impact on the transcriptional network of endocrine pancreas progenitors.
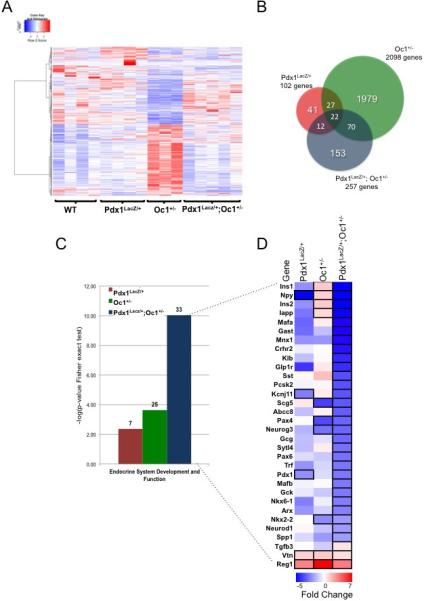
(A) Hierarchical clustering of 2331 differentially expressed genes in individual pancreata at e15.5 from Pdx1LacZ/+ (n=4), Oc1+/− (n=3), and Pdx1LacZ/+;OC1+/− mice (n=5) compared to WT (n=4); (B) Venn diagram depicting the number of altered genes in the Pdx1LacZ/+, Oc1+/− and Pdx1LacZ/+;Oc1+/−; (C) Endocrine system development and function gene ontology category in each genotype, according to negative log of p-value from Fisher exact test. The numbers above each column represent the number of genes enriched in each category; (D) Heat map of endocrine development and function genes. Up- or down-regulated genes with false discovery rate less than 0.1 and fold change higher than 0.5 versus WT are highlighted with bold black borders. (See also Tables S1 and S2)
