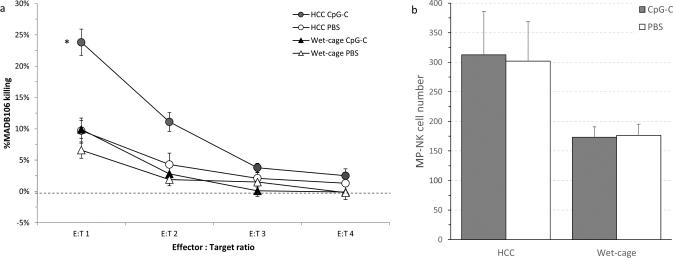
Fig. 7. Wet-cage stress concurrently with CpG-C treatment prevented the increase in marginating-pulmonary (MP)-NK ex-vivo cytotoxicity against MADB106 tumor cells.
(a) MP-NK activity: CpG-C markedly elevated MADB106 killing levels in home cage control (HCC) animals, but not in animals subjected to the wet cage condition. (b) MP-NK cell number: No significant effects of CpG-C were evident, suggesting that the increase in NK activity levels evident in (a) are per cell. Data is shown as mean ± SEM.