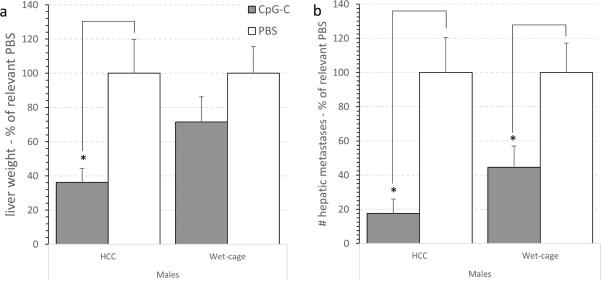
Fig. 9. Wet-cage stress exposure concurrently with CpG-C treatment attenuated its beneficial effects on liver weight and number of CT26 metastases in males.
(a) CpG-C significantly reduced liver weight in HCC (*), but not in animals subjected to the wet cage condition. Weight is shown as % of relevant PBS group. (b) Assessing the number of metastases yielded a significant effect for CpG-C in reducing metastases number under HCC (*), which was partially attenuated under the wet cage condition (*). Number of metastases is shown as % of relevant PBS group. * indicates a significant difference from PBS at p < 0.05. In both indices (a) and (b). Data is shown as mean ± SEM.