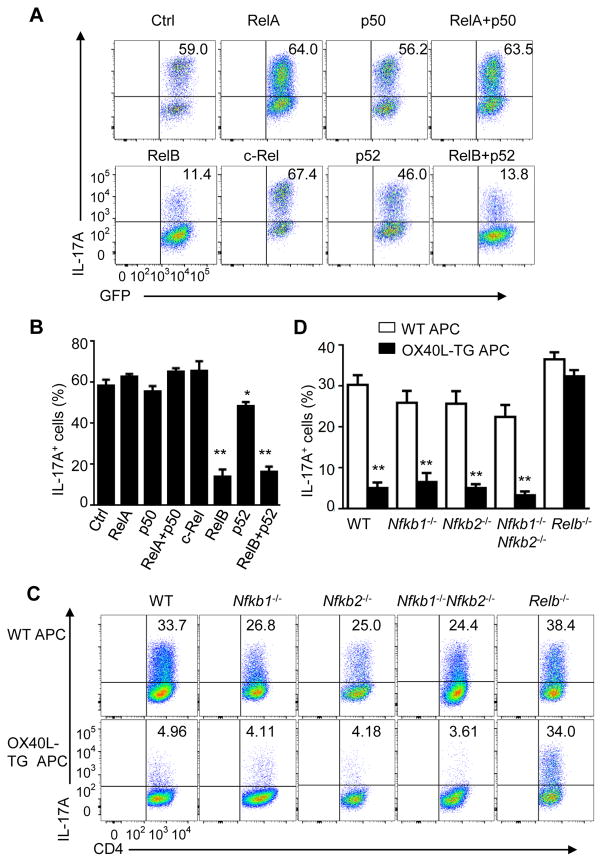
Figure 3. Critical role of RelB in suppression of Th17 cells by OX40.
(A and B) Induction of Th17 cells from WT CD4+ T cells transduced with empty vector encoding GFP alone (Ctrl) or with retrovirus expressing p50, RelA, p52, c-Rel, or RelB, and cultured for 3 days under Th17-polarizing conditions (A). Graphs in (B) depict Mean ± SEM of 5 experiments with triplicate cultures. * p <0.05; ** p <0.01.
(C and D) Induction of Th17 cells from WT B6, Nfkb1−/−, Nfkb2−/−, −/−, Nfkb1−/−Nfkb2−/− DKO, and Relb−/− CD4+ T cells activated for 3 days as in Figure 1D(C). Graphs in (D) depict Mean ± SEM of 5 experiments with triplicate cultures. ** p <0.01.