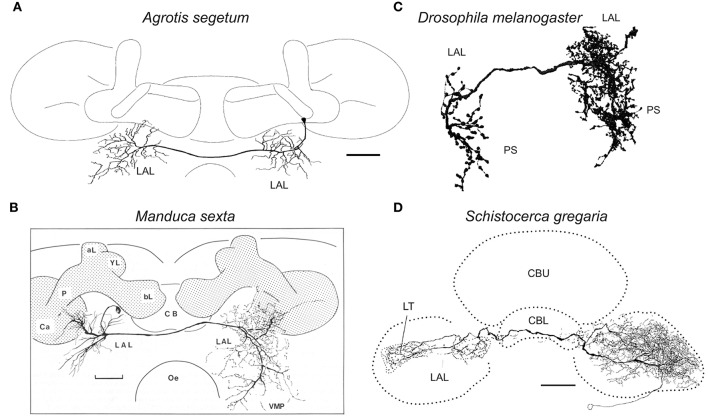
Figure 8.
Comparison of neuronal morphology of the LAL bilateral neurons across species. (A) LAL bilateral neuron of the turnip moth Agrotis segetum (Lei et al., 2001). (B) LAL bilateral neuron of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta (Kanzaki et al., 1991b). (C) LAL bilateral neuron of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster (Fru-M-200330, FlyCircuit Database; Chiang et al., 2011). The neuron has smooth processes in the ipsilateral LAL, epaulete, wedge, vest and superior posterior slope and varicose processes in the contralateral LAL, inferior posterior slope and superior posterior slope. (D) LAL bilateral neuron of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria (Heinze and Homberg, 2009). Scale bars, 50 μm for (A), 100 μm for (B,D). aL, alpha-lobe of the mushroom body; bL, beta-lobe of the mushroom body; Ca, calyx of the mushroom body; CB, central body; CBL, lower division of the central body; CBU, upper division of the central body; LAL, lateral accessory lobe; LT, lateral triangle; Oe, esophagus; P, pedunculus of the mushroom body; PS, posterior slope; VMP, ventral-medial protocerebrum.