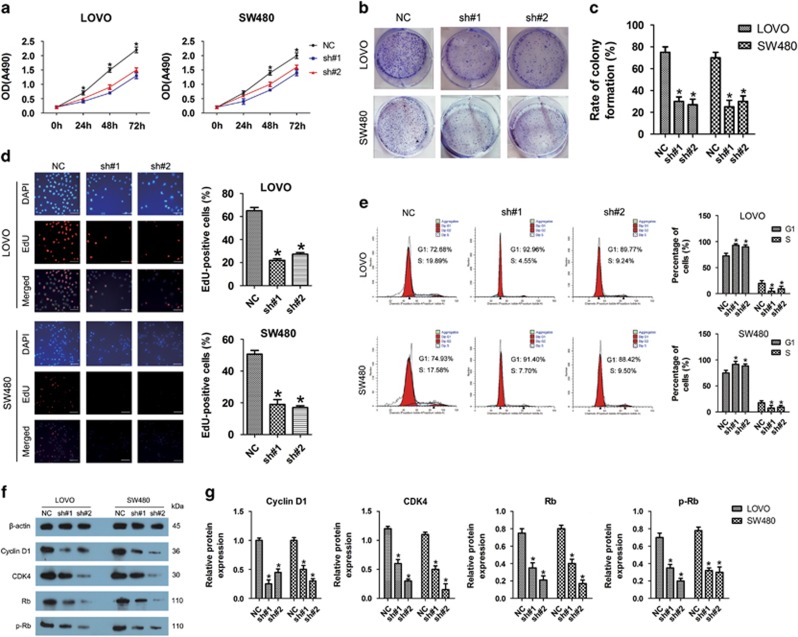
Figure 3.
Linc-UFC1 knockdown inhibited proliferation of CRC cells via cell cycle arrest. (a) Knockdown of linc-UFC1 impaired proliferation in LOVO and SW480 cells, as revealed by CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation assay (n=6; *P<0.05 versus sh#1 and sh#2). (b and c) Histological analysis of the rates of colony formation in control (NC) and linc-UFC1 knockdown groups (sh#1 and sh#2; n=6; *P<0.05 versus NC). (d) The EdU incorporation assay to examine the effects of linc-UFC1 inhibition on DNA synthesis during cell growth. The images were taken at × 200. The result showed that the proportion of S phase cells (EdU-positive cells) was decreased in shRNA-treated groups (n=6, P<0.05 versus NC). (e) Flow cytometric analysis of cell cycle arrest 48 h after treatment with shRNAs (sh#1 and sh#2) and negative control (NC) in LOVO and SW480 cells (n=6, P<0.05 versus NC). (f and g) The expression levels of cell cycle-related proteins (cyclin D1, CDK4, Rb and p-Rb) indicated by western blotting in control (NC) and linc-UFC1 knockdown groups of LOVO and SW480 cells (n=6; *P<0.05 versus NC)