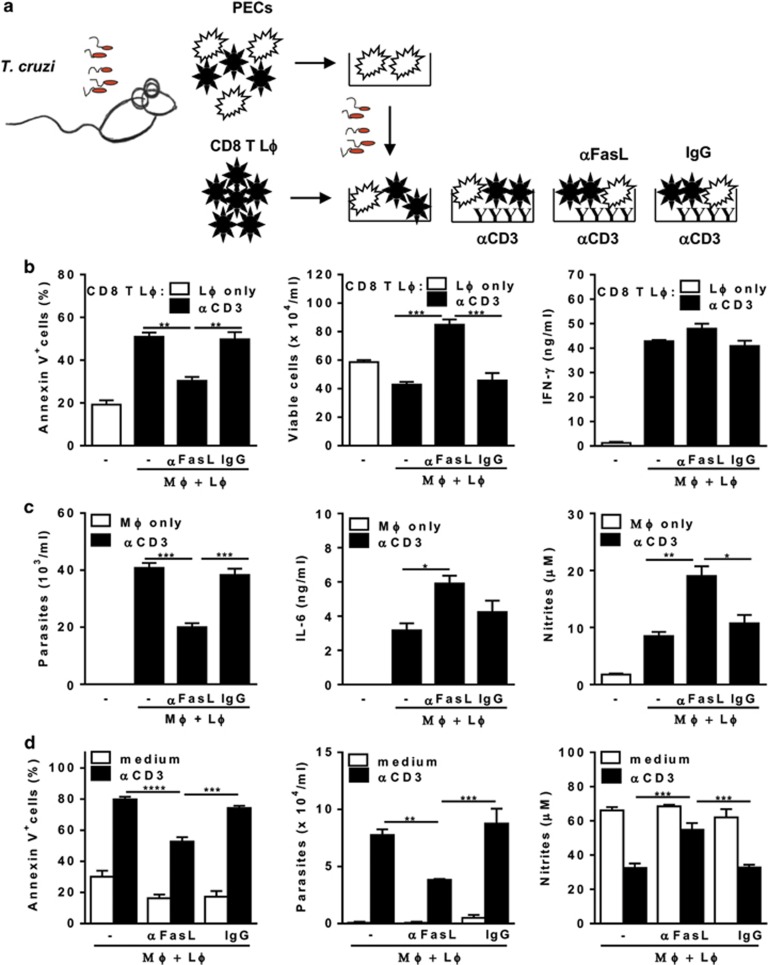
Figure 3.
FasL-mediated apoptosis of CD8 T cells drives T. cruzi infection in cocultured macrophages. (a–d) Peritoneal macrophages from infected (18 dpi) mice were infected with T. cruzi and cocultured with purified splenic CD8 T cells from infected (18–20 dpi) mice in the presence of interleukin-2 (IL-2). Cocultures were stimulated or not with soluble anti-CD3 and treated or not with anti-FasL or control immunoglobulin G (IgG). (b–d) After 48 h, culture supernatants were collected for NO or cytokine responses. (b and d) CD8 T cells were collected for detection of apoptosis by annexin V and 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD) staining. (c and d) Adherent cells were cultured during 2–3 weeks for determination of parasite burden, as released trypomastigotes. Data are expressed as means and S.E.M. of three technical replicates. Each set of data (b–d) represents at least three independent experiments. Significant differences between treatments in anti-CD3 activated cultures are indicated (*), as analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) (b and c) or by two-way ANOVA (d) with Tukey's post-test