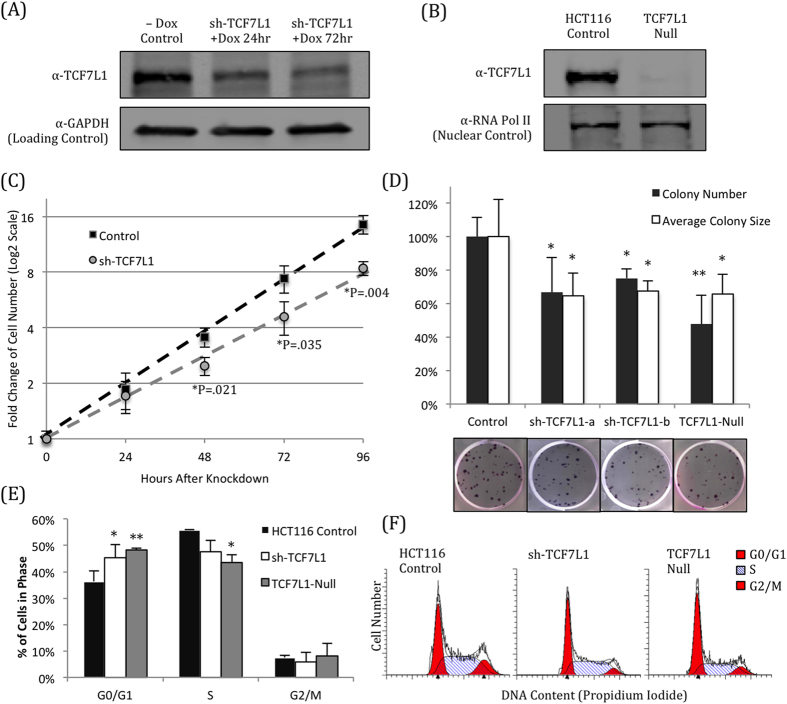
Figure 2. Loss of TCF7L1 reduces HCT116 cell growth and proliferation.
(A) shRNA-mediated knockdown of TCF7L1 reduces protein expression within 24 hours of induction by addition of doxycycline (Dox). (B) CRISPR/Cas9 was used to completely eliminate TCF7L1 protein expression, without inhibiting expression of other TCF/LEF factors (Supplementary Fig. S2). (C) TCF7L1 knockdown significantly slowed the growth of HCT116 cells within 48 hours of shRNA induction. (D) HCT116 cells with reduced (sh-TCF7L1) or eliminated (TCF7L1-Null) expression of TCF7L1 had significantly reduced colony growth (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared to Control). These cells formed fewer colonies with a smaller average colony size. Representative images are shown below quantification. Average and standard deviation were calculated across three independent experiments with at least three replicates each. (E) Loss of TCF7L1 affected cell cycle progression, causing a significant increase in G0/G1-phase cells, with a concomitant reduction in S-phase. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 compared to HCT116 control for the respective cell cycle phase.) (F) Representative cell cycle images generated with ModFit.