Fig. 3.
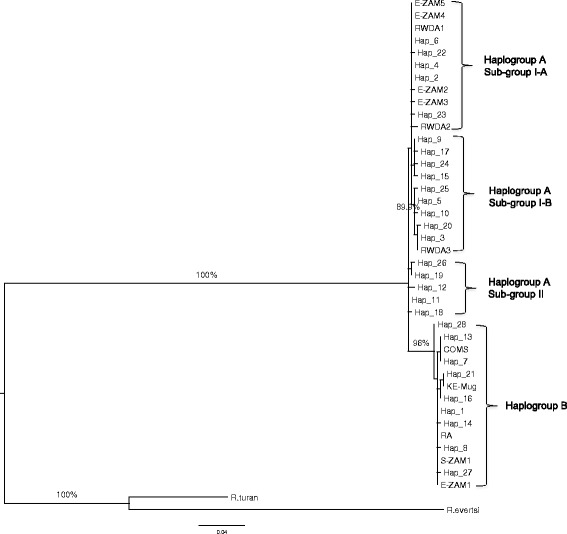
Tree showing the phylogenetic relationships between the Kenyan COI haplotypes and sequences generated by Mtambo et al. [17]. Eleven sequences from GenBank were included in the analysis. Five were from eastern Zambia [accession number DQ859261 (E-ZAM1); DQ859263 (E-ZAM2); DQ859264 (E-ZAM3); DQ859265 (E-ZAM4) and DQ859266 (E-ZAM5)], one from southern Zambia [DQ859262 (S-ZAM1)], three from Rwanda [DQ901360 (RWDA1), DQ901362 (RWDA2), DQ901363 (RWDA3)], one from Comoros Island [DQ901357 (COMS)] and one from Kenya [DQ901358 (KE-Mug)]. Another R. appendiculatus sequence [AF132833 (RA)] was included in the analysis as a reference while a sequence from R. turanicus [JQ737086 (R. turan)] was used as the outgroup. Percent bootstrap values above 75 % are shown
