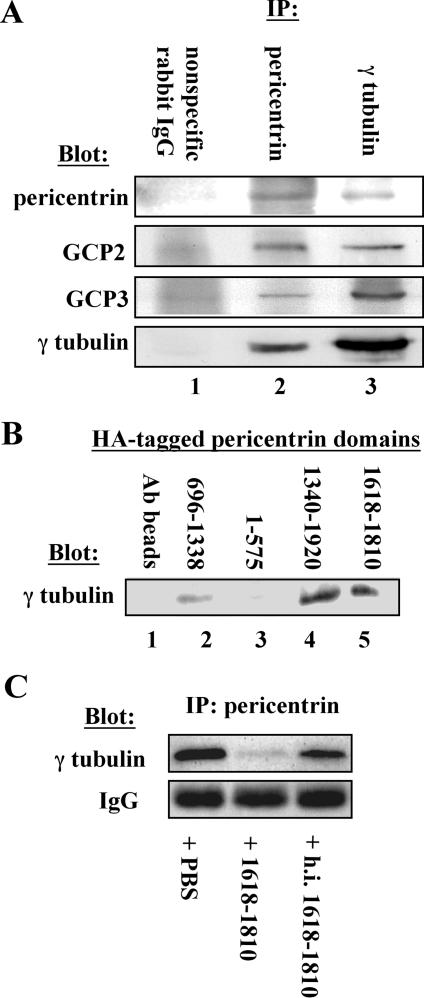
Figure 2.
Pericentrin interacts with the γ TuRC in Xenopus extracts. (A) Immunoprecipitation of endogenous pericentrin pulls down γ TuRC proteins (γ tubulin, GCP2, and GCP3) from Xenopus extracts (lane 2) and immunoprecipitation of γ tubulin pulls down pericentrin (lane 3), whereas nonspecific rabbit IgG precipitates none of these proteins (lane 1). (B) HA-tagged C-terminal domains of pericentrin bound to anti-HA beads pull down endogenous γ tubulin from Xenopus extracts (lanes 4 and 5), whereas beads alone and HA-tagged central and amino-terminal domains do not pull down significant γ tubulin (lanes 1–3). (C) A C-terminal domain of pericentrin (1618–1810) disrupts the interaction between endogenous pericentrin and the γ TuRC in extracts as shown by immunoprecipitation with anti-pericentrin antibodies, whereas heat-inactivated protein (h.i. 1618–1810) and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) have no effect. Numbers in B and C represent amino acid numbers of pericentrin.