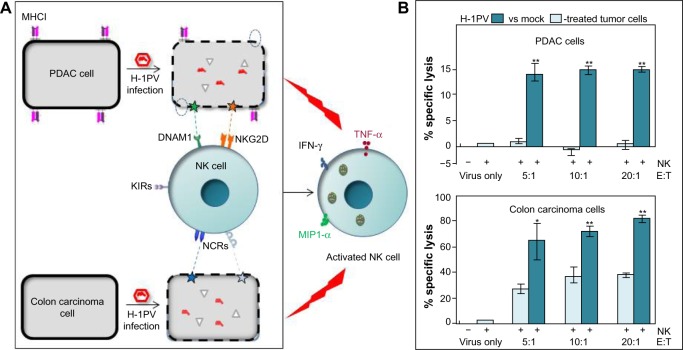
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of the indirect immunostimulating effects of protoparvovirus H-1PV on human NK cells.
Notes: (A) H-1PV-infected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and colon carcinoma cells were cocultivated with IL-2-stimulated NK cells. Contact with virus-infected tumor cells triggered NK cell activation, resulting in the production of cytokines and chemokines, including IFN-γ, TNF-α, and MIP1-α. This activation was traced back to the downregulation of MHCI (dotted circles) and an upregulation of NK-cell-activating ligands (stars). (B) Activated NK cells (E) showed a strikingly enhanced capacity for killing cocultured PDAC and colon carcinoma target cells (T). *P<0.05; **P<0.01.
Abbreviations: H-1PV, H-1 parvovirus; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; NK, natural killer; MIP1-α, macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha; KIRs, killer inhibitory receptors; NCRs, natural cytotoxicity receptors; DNAM-1, DNAX accessory molecule-1; NKG2D, natural-killer group 2, member D.