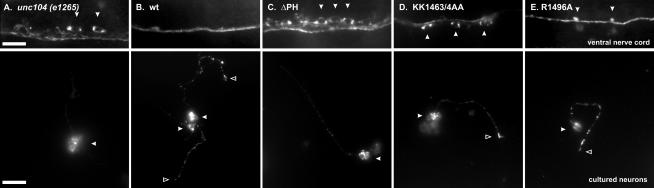
Figure 4.
Synaptotagmin localization in C. elegans and in neurons in culture. Top: Synaptotagmin (a synaptic vesicle marker) localization in the ventral nerve cord of unc104 (e1265) animals and in unc-104 animals expressing wt UNC-104, UNC-104ΔPH, UNC-104KK1463/4AA, or UNC-104R1496A motor proteins. In the unc104 animals, the staining is mostly confined to neuronal cell bodies (examples indicated by arrows) with a weak staining in the axons running horizontally in the cord, indicating a failure to transport synaptic vesicles. On the other hand, animals expressing wt UNC-104 have robust axonal staining in the ventral nerve cord. The UNC-104ΔPH and UNC-104KK1463/4AA-expressing animals also show retention of synaptic vesicles in neuronal cell bodies (arrows). Scale bar, 10 μm. Bottom: Synaptotagmin localization in primary cell culture neurons derived from the worms shown on the left half. While wt UNC-104 and the point mutation–expressing animals show considerable staining in the neurites and often at neurite tips, the unc104 and UNC-104ΔPH–expressing animals, on the other hand, tend to have decreased staining in the neurite (particularly at tips) but accumulated staining in the cell body. Cell bodies are indicated by arrows. Scale bar, 10 μm.