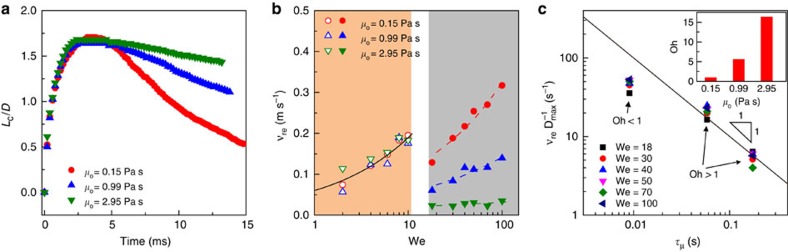
Figure 5. Substrate-dependent retraction dynamics.
(a) Comparison of time-resolved evolution of the spread factor Lc/D on samples of h=50 μm with different viscosity. The We is 20. The values of Lc/D in the retraction stage are dependent on the oil viscosity, displaying a substrate-dependent retraction behaviour. (b) Calculated retraction velocity νre as a function of We indicating that the retraction velocity is independent of the oil viscosity in the superhydrophobic-like bouncing regime, that is, We≲10. By contrast, with the rupture of thin air cushion, that is, We≳18, the retraction velocity becomes highly dependent on the oil viscosity. (c) The droplet retraction rate νre/Dmax as a function of viscous time scale τμ. The measured retraction rates 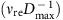 overlap well with the scaling of
overlap well with the scaling of 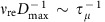 , where
, where 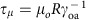 is the viscous time scale (corresponding to two datasets with Oh>1). For Oh≈0.86 (μo=0.15 Pa s), the retraction rates diverge from the master curve because the inertia force and viscous force are comparable in this case.
is the viscous time scale (corresponding to two datasets with Oh>1). For Oh≈0.86 (μo=0.15 Pa s), the retraction rates diverge from the master curve because the inertia force and viscous force are comparable in this case.