Figure 2.
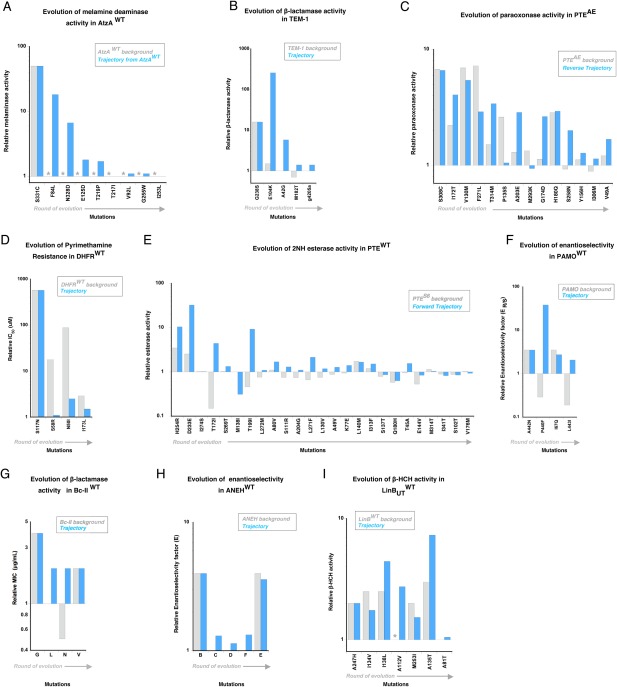
Functional changes caused by the mutations fixed within nine adaptive trajectories. The fold change in enzyme function, induced by mutations, is depicted as a bar, on the wild‐type background (grey) and as it occurs in the evolutionary trajectory (blue). Evolution of (A) melamine deaminase activity in AtzA, (B) β‐lactamase activity in TEM‐1, (C) paraoxon hydrolysis in PTEAE (reverse trajectory), (D) pyrimethamine binding in DHFR, (E) 2NH hydrolysis in PTEWT (forward trajectory), (F) enantioselectivity in PAMO (G) β‐lactamase activity in Bc‐II, (H) enantioselectivity in ANEH and (I) haloalkane dehydrogenase activity in LinBUT. Mutations are ordered according to their occurrence in the trajectory (from left to right). Detailed values are provided in Supporting Information Table S1. Non‐detectable activity/binding levels are shown as grey stars.
