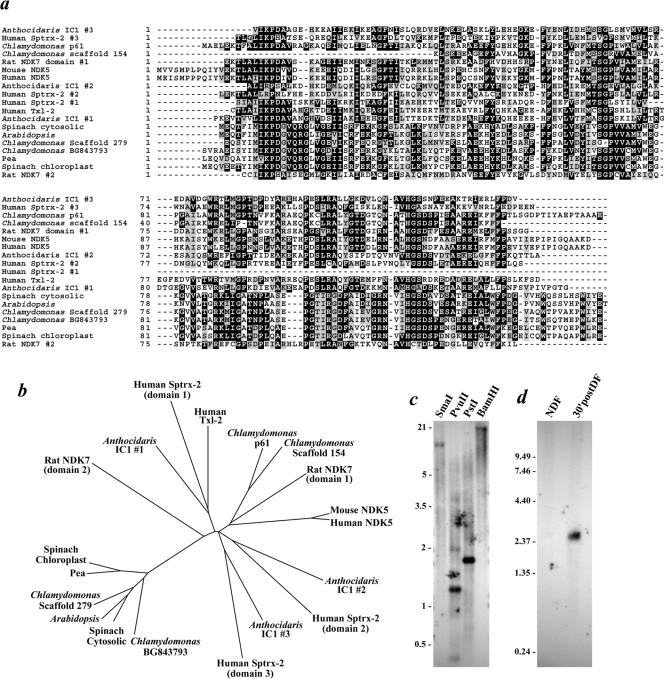
Figure 1.
NDK phylogeny and Northern/Southern blot analysis of p61. (a) Chlamydomonas ESTs AV645300 (encoding p61) and BG843793, the NDKs identified in scaffolds #154 and 279 of the Chlamydomonas genome, the NDK modules from the IC1 polypeptide of sea urchin dynein (Anthocidaris crassispina), human and murine NDK5, rat NDK7, human Sptrx-2, human Txl-2, and the cytosolic and chloroplast NDKs from spinach, pea, and Arabidopsis were aligned using ClustalW. Residues conserved in ≥30% of the sequences were shaded using BOXSHADE. (b) ClustalW alignment was used as the input to generate the neighbor-joining unrooted tree shown. The BG843793 EST and NDK encoded on scaffold 279 clearly group with the NDKs of higher plants. In contrast, AV645300 (p61) and the scaffold #154–9 NDK (p40) are more closely related to the testis-specific mammalian enzymes. (c) Southern blot analysis of Chlamydomonas genomic DNA restricted with SmaI, PvuII, PstI, and BamHI and probed with the 5′ region of the AV645300 EST clone. Single bands were detected in the SmaI-, PstI-, and BamHI-digested samples. (d) Northern analysis of Chlamydomonas RNA obtained from non-deflagellated cells (NDF) and from cells that had undergone flagella excision and been allowed to regenerate new flagella for 30 min (30′postDF). A 2.54-kb mRNA that is highly up-regulated after deflagellation was detected by the AV645300 probe.