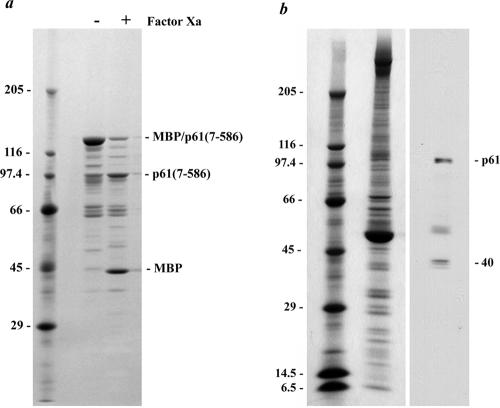
Figure 4.
p61 migrates anomalously in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. (a) Twenty micrograms of the MBP-p61(7-586) fusion protein was electrophoresed in a 5–15% acrylamide gradient gel, both before and after incubation with factor Xa, and stained with Coomassie Blue. The intact fusion protein has a calculated mass of 103,130 Da but migrated with Mr ∼135,000. The minor bands derive from cleavage of MBP-p61(7-586) by endogenous bacterial proteases. After factor Xa cleavage of the fusion protein, MBP migrated at ∼Mr 40,000 as observed previously, whereas the p61(7-586) segment (calculated mass 60,662 Da) had Mr ∼100,000. (b) Wild-type axonemes (∼100 μg) prepared in the presence of a protease inhibitor cocktail were electrophoresed in a 5–15% acrylamide gradient gel and either stained with Coomassie Blue (left) or blotted and probed with the CT220 antibody (right). Two prominent bands of Mr102,000 and 40,000 were obtained. The top band corresponds to p61, which migrates anomalously. The diffuse band located above tubulin is a proteolytic fragment of p61.