Figure 6.
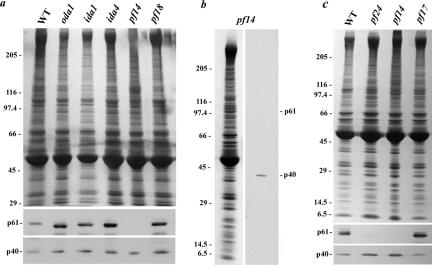
p61 is missing in mutant axonemes lacking radial spokes. (a) Axonemes were obtained from wild-type Chlamydomonas (WT) and from mutants lacking outer (oda1) and inner (ida1 and ida4) dynein arms, radial spokes (pf14), and the central pair microtubule complex (pf18). After electrophoresis, samples were stained with Coomassie Blue (top) or examined for CT220 immunoreactivity (bottom). The Mr 40,000 protein (p40) was detected in all samples, whereas p61 was absent only in pf14 axonemes. (b) Axonemes from the pf14 mutant were prepared in the presence of a comprehensive protease inhibitor cocktail. The sample was electrophoresed and stained with Coomassie Blue (left) or blotted and probed with CT220 (right). These axonemes contain the Mr 40,000 band. However, p61 and its breakdown product migrating just above tubulin (see Figure 4b) were missing. (c) To assess the location of p61 within flagellar radial spokes, axonemes were prepared from wild type, pf14, pf17 (lack the spoke head), and pf24 (no spoke head and truncated stalk) axonemes. The p61 protein was present in pf17, but levels were drastically reduced in pf24 (upon prolonged exposure, a very weak p61 band was detected in this mutant). This suggests that p61 is located within the distal portion of the radial spoke stalk.