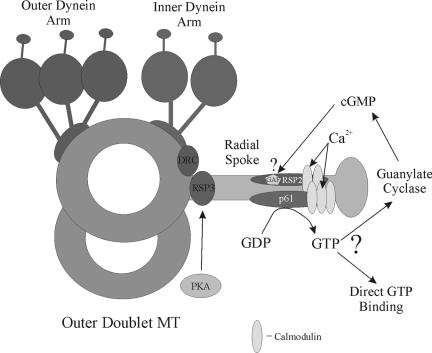
Figure 9.
Model for Ca2+-dependent GTP signaling through the radial spokes. The diagram illustrates the location of structures associated with a single flagellar doublet microtubule. Within the radial spoke stalk, RSP3 is located at the base and is thought to anchor cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), resulting in phosphorylation of inner dynein arm proteins. The p61 protein and associated calmodulin (CaM) are also present in the stalk. Ca2+ binding results in activation of the p61 NDK module to generate GTP (or some other NTP), which subsequently could be used either by a GTP-binding switch protein, a specific GTPase or a guanylate cyclase. Intriguingly, the calmodulin-associated RSP2 protein, which contains a GAF domain that might potentially bind cGMP and act as a downstream target for p61-generated GTP, is also a component of the radial spoke (Yang et al., 2004) and is apparently located close to p61. The dynein regulatory complex (DRC) is located near the base of the radial spokes and inner arms.