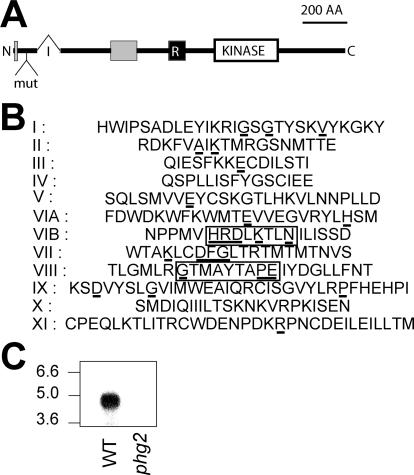
Figure 1.
Structure of the Phg2 protein. (A) Organization of the Phg2 protein. The position of an intron (I) in the genomic sequence is indicated (321 nucleotides downstream from the start codon). In the phg2 mutant, the mutagenic plasmid (mut) is inserted in the first exon, encoding the N-terminal portion of Phg2. The Phg2 protein contains a putative kinase domain (KINASE), a putative ras-binding domain (R), and two proline-rich domains (gray boxes). (B) Organization of the Phg2 kinase subdomains (residues 802-1074): the residues most conserved in kinase domains are underlined. Residues indicating a serine/threonine- rather than a tyrosine-kinase activity are boxed. (C) Cellular RNA was extracted from wild-type (WT) or phg2 mutant cells, migrated on an agarose gel, transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane, and revealed with a probe corresponding to the 3′ end of the PHG2 coding sequence. A 4.5-kb transcript was detected in wild-type but not in phg2 mutant cells. The sequence data are available from European Molecular Biology Laboratory database under accession no. AJ585374.