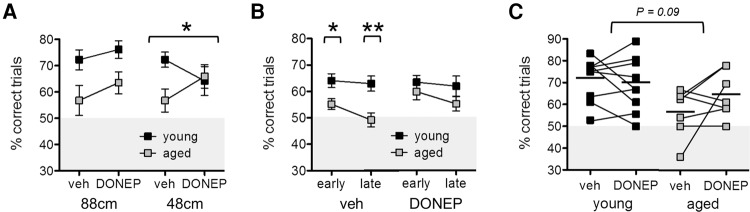
Figure 5.
Spatial discrimination performance after systemic donepezil injections. (A) No age difference was present in the effect of donepezil injections on 88-cm trials (P = 0.63); however, donepezil differentially influenced performance of young and aged rats on 48-cm trials (P < 0.04). Aged rats showed improvement with donepezil (mean change from vehicle = +9.14%, SD = 13.5), while young rats showed decreased performance (mean change from vehicle = −8.04%, SD = 17.2). Data from 15-cm trials were excluded from analyses because performance remained consistently at chance across all experimental conditions. (B) Performance on easy versus late discrimination trials after vehicle or donepezil injections. Donepezil improved performance across both early and late phases in aged rats such that significant impairments observed after vehicle injections (Ps < 0.02) were alleviated (Ps > 0.21). (C) To test whether donepezil had a more general cognitive-enhancing effect, percent correct responses were collapsed across 88-cm and 48-cm trials. Individual performance is shown for young rats (left; black markers) and aged rats (right; gray markers); horizontal lines indicate group means. A statistical trend indicated that, overall, aged rats tended to benefit from donepezil treatment (mean change from vehicle = +7.9%, SD = 14) while young rats did not (mean change from vehicle = −2.1%, SD = 9.5; P = 0.09). Graphs show means ± SEMs. (*) P < 0.05 (**) P < 0.01.