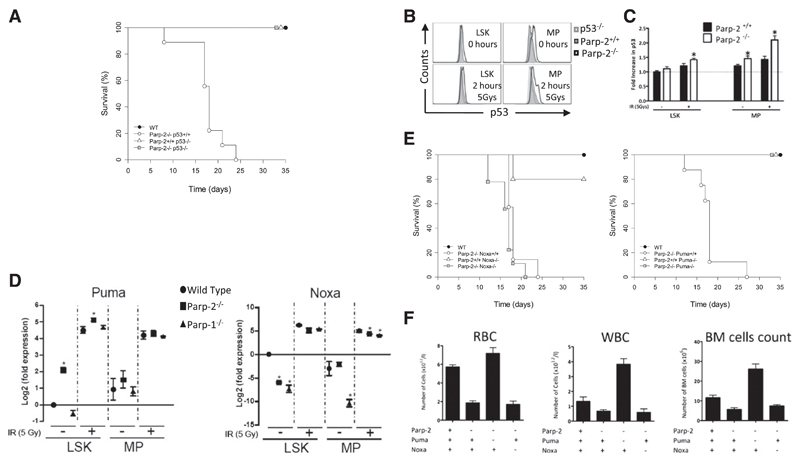
Figure 5. Effect of p53-mediated apoptotic pathways in the radiosensitivity of Parp-2 deficient mice.
(A) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for 5-week-old WT (n = 12), Parp-2−/−p53+/+ (n = 13), Parp-2+/+p53−/− (n = 6), and Parp-2−/−p53−/− (n = 5) mice after a single dose of TBI (5 Gy). (B) Representative histograms show p53 protein levels in LSK and MP cells derived from Parp-2+/+ and Parp-2−/− mice at basal level and 2 hours after γ-irradiation (5 Gy). LSK and MP cells from p53−/− mice were included as controls. (C) The relative p53 protein levels were calculated on the basis of the mean fluorescence intensity and were presented as fold induction compared with WT cells. Bars represent the mean ± SEM obtained from 4 mice per genotype. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Puma and Noxa mRNA expression levels in LSK and MP cells derived from WT, Parp-2−/−, and Parp-1−/− mice at basal level and 2 hours after γ-irradiation (5 Gy). Samples were normalized according to p-actin expression levels. Results are expressed as log2-fold expression compared with levels measured in untreated WT LSK cells. Values represent the mean ± SEM obtained from 3 independent experiments. *Statistically significant difference (P < .05). (E) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for 5-week-old WT (n = 12), Parp-2−/−Noxa+/+ (n = 13), Parp-2+/+ Noxa−/− (n = 5), Parp-2−/−Noxa−/− (n = 9), Parp-2−/−Puma+/+ (n = 13), Parp-2+/+Puma−/− (n = 6), and Parp-2−/−Puma−/− (n = 9) mice after a single dose of TBI (5 Gy). Survival was monitored for 35 days. (F) Graph showing peripheral RBCs, WBCs, and total number of BM cells (2 femurs per mouse) in the different genotypes at day 12 post irradiation (5 Gy). Values represent the mean ± SEM of at least 6 mice of each genotype.