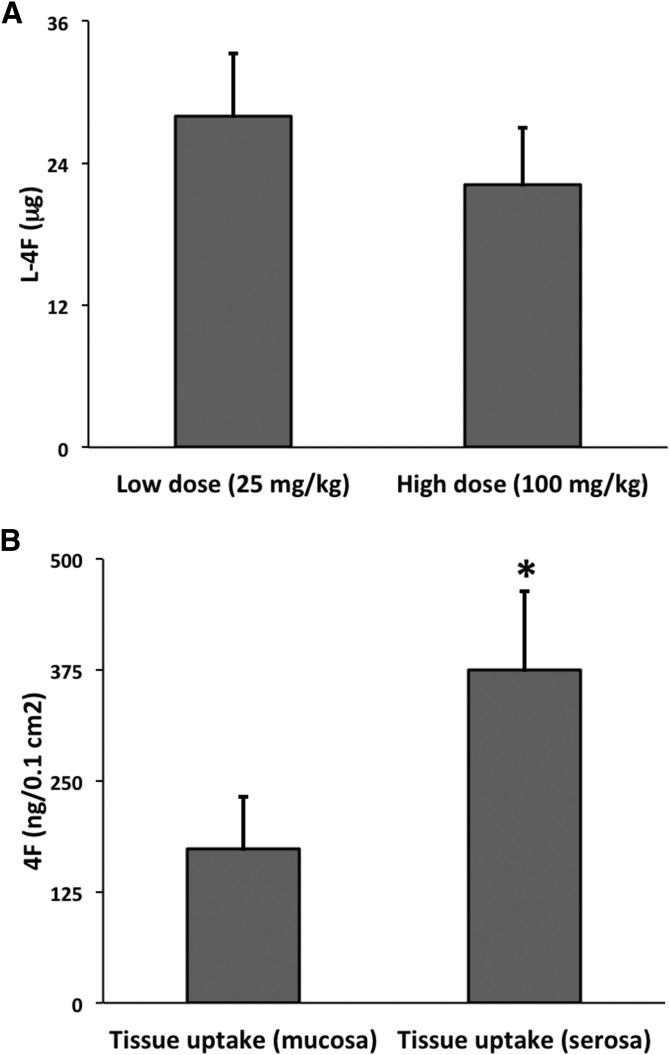
Fig. 4.
The process of l-4F secretory transport is saturable, while in turn luminal-side l-4F can itself be taken up into the SI tissue. A: Low-does (25 mg/kg) and high-dose (100 mg/kg) l-4F was introduced via tail vein into C57BL/6J mice (n = 4 and 6, respectively). After 1 h, the level of l-4F in the SI lumen rinse was determined by LC/MS/MS. No significant difference was found between the two doses (P = 0.4), indicating that the secretory transport pathway is saturable. B: l-4F or 14C-l-4F + l-4F was added to either the mucosal or serosal media of the Ussing chamber, and uptake by the tissue was determined by LC/MS/MS or scintillation counting respectively (n = 7/group). Duodenal explants took up significantly more 4F from the serosal media than from the mucosal media (* P < 0.005). Error is reported as SEM.