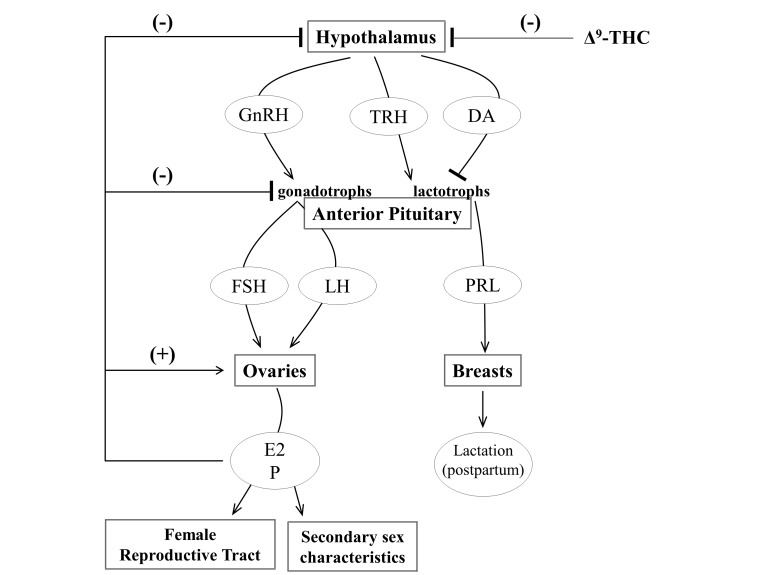
Figure 3.
A simplified representation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis. Hypothalamic stimulation elicits the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), and dopamine (DA) onto the anterior pituitary, which contains specialized neurons that are sensitive to these hormones. TRH stimulates and dopamine inhibits the release of prolactin (PRL) from the lactotrophs of the anterior pituitary. Prolactin promotes milk production during the postpartum period. GnRH stimulates the release follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from gonadotrophs in the anterior pituitary. FSH and LH promote the ovarian production of estrogen (primarily estradiol, E2), development of mature ovarian follicles, the release of oocytes from the mature ovarian follicles during ovulation and the production of progesterone (P) from the post-ovulatory follicle. The ovarian hormones, particularly E2, signal at the ovaries to promote follicle maturation. The ovarian hormones also exert negative feedback on the pituitary and hypothalamus to decrease release of FSH, LH and GnRH.