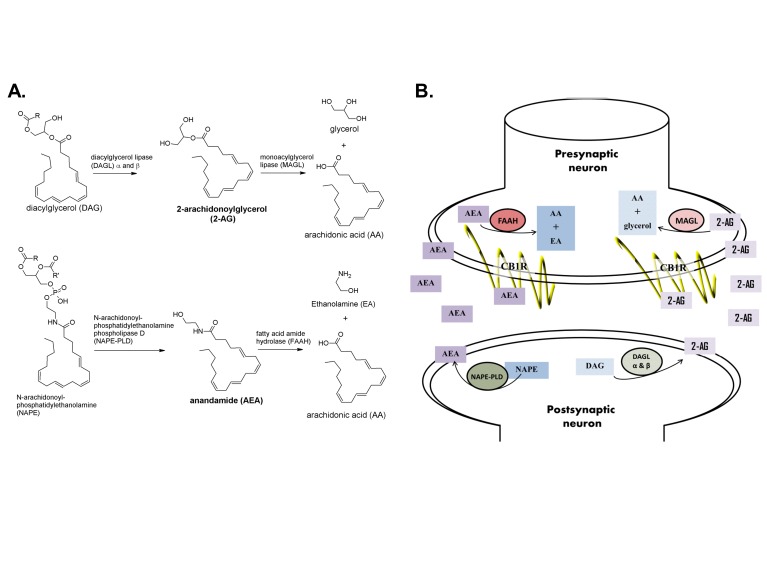
Figure 5.
Formation, degradation and retrograde signaling of endocannabinoids. A. The eCB 2-AG is formed primarily from DAG by DAGL-α and DAGL-β and is degraded by MAGL into AA and glycerol. The eCB AEA is formed primarily from NAPE by NAPE-PLD and degraded to AA and EA by FAAH. B. Neuronal eCB signaling occurs by retrograde processes; that is, eCBs are made in the postsynaptic neuron, passively diffuse out of the neuron, through the synaptic cleft and bind to cannabinoid receptors on pre-synaptic axonal terminals. eCBs activate CB1R, which tends to have an inhibitory, hyperpolarizing effect on the presynaptic neuron. The formation of eCBs is stimulated by increased signaling from the presynaptic neuron. Retrograde eCB signaling acts to suppress presynaptic neuronal activity by depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition (DSI, in GABAergic neurons) or depolarization-induced suppression of excitation (DSE, in glutamatergic neurons). Structures obtained from [65-67].