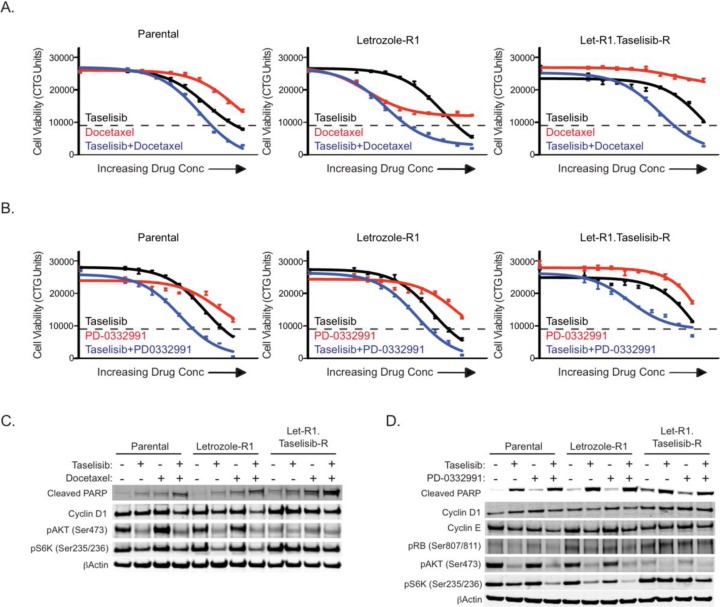
Figure 5. Dual resistant cells are still sensitive to taselisib in combination with docetaxel or CDK4/6 inhibition.
(A) Taselisib combines well with docetaxel in MCF7-ARO cells. The effect on viability of taselisib and docetaxel as single agents is shown in the black and red lines, respectively. The combination effect of the two drugs is indicated with the blue line. Starting doses for taselisib were 80 nM for the parental and letrozole-R1 lines and 10 μM for taselisib for Let-R1.GDC-0032-R. Docetaxel starting doses were 36 nM for all three lines. (B) Taselisib combines well with PD-0332991 in MCF7-ARO cells. The effect on viability of taselisib and PD-0332991 as single agents is shown in the black and red lines, respectively. The combination effect of the two drugs is indicated with the blue line. Starting doses for taselisib were 80 nM for the parental and letrozole-R1 lines and 10 μM for dual-resistant. PD-0332991 starting doses were 10 μM for all three lines. (C) Increased apoptosis is observed with the taselisib and docetaxel combination in cells sensitive or resistant to taselisib and letrozole. Immunoblots from samples treated for 24 hours with 20 nM taselisib (Parental and Letrozole-R1) or 2.5 μM (Let-R1.Taselisib-R) and/or 9 nM docetaxel. (D) Increased growth arrest is observed with combined PI3K and CDK4/6 inhibition. Immunoblots from samples treated for 24 hours with 20 nM taselisib (Parental and Letrozole-R1) or 2.5 μM (Let-R1.Taselisib-R) and/or 2.5 μM PD-0332991. Dotted lines for all viability data are indicative of CTG counts at the beginning of drug treatment. Error bars indicate standard deviation around the mean.