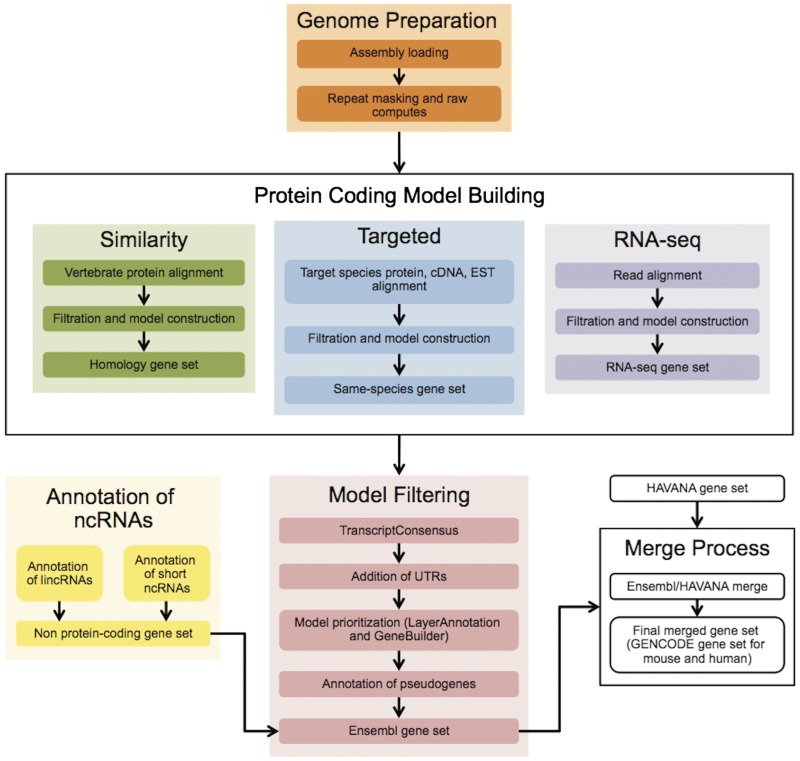
Figure 1.
The Ensembl Genebuild workflow for annotating genes. The first phase of the annotation process is the Genome Preparation stage, which prepares the genome for gene annotation. The second phase is the Protein-coding Model Building stage, consisting of the Similarity, Targeted and RNA-seq pipelines. This generates a large set of potential protein-coding transcript models by aligning biological sequences to the genome and then inferring transcript models (exon–intron structures) using the alignments. Noncoding genes are annotated separately. Usually, the final phase is the Model Filtering stage. This involves sorting through the potential coding transcript models and filtering out those that are not well supported. Pseudogenes are then annotated and the noncoding RNA genes are incorporated to create the Ensembl gene set, which is then cross-referenced with external data sources. For some species (human, mouse, rat, zebrafish and pig) the HAVANA group produces manually curated gene sets. These annotations are merged with our Ensembl gene set to produce the final merged gene set. In the case of mouse and human, the merged sets comprise the GENCODE sets of genes.