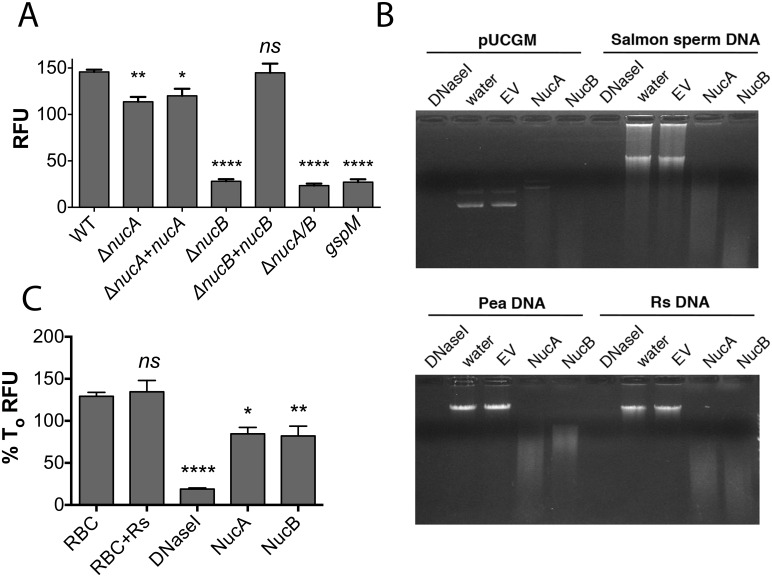
Fig 4. R. solanacearum genes encode two secreted DNases.
(A) DNase activity of cell-free bacterial culture supernatant from R. solanacearum strains grown in minimal medium, measured by DNase Alert assay on a fluorescence plate reader at 37°C over 3 h. Bars represent mean relative fluorescence units normalized to A600 of overnight culture. (B) Activity of purified nucleases on different DNA substrates. 1 μg of purified NucA or NucB were incubated with 1 μg of each DNA substrate: R. solanacearum genomic DNA, pea DNA, supercoiled plasmid DNA (pUCGM) and salmon sperm DNA) for 30 min at 37°C. Results were analyzed by electrophoresis in a 1% agarose gel. (C) NucA and NucB degrade DNA from root border cell traps. Pea border cells were incubated with R. solanacearum in the presence of NucA, NucB or DNase I as control. Relative DNA amount was measured by SYTOX Green fluorescence after 6 h of incubation. Asterisks indicate differences from the wild-type (one-way ANOVA, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001). Abbreviations: WT, wild-type strain; ΔnucA, R. solanacearum nucA mutant; ΔnucB, R. solanacearum nucB mutant; ΔnucA/B, R. solanacearum double nuclease mutant; nucBcom or nucBcom; R. solanacearum mutant complemented with the corresponding wild-type gene; RBC, root border cells; Rs, R. solanacearum cells.