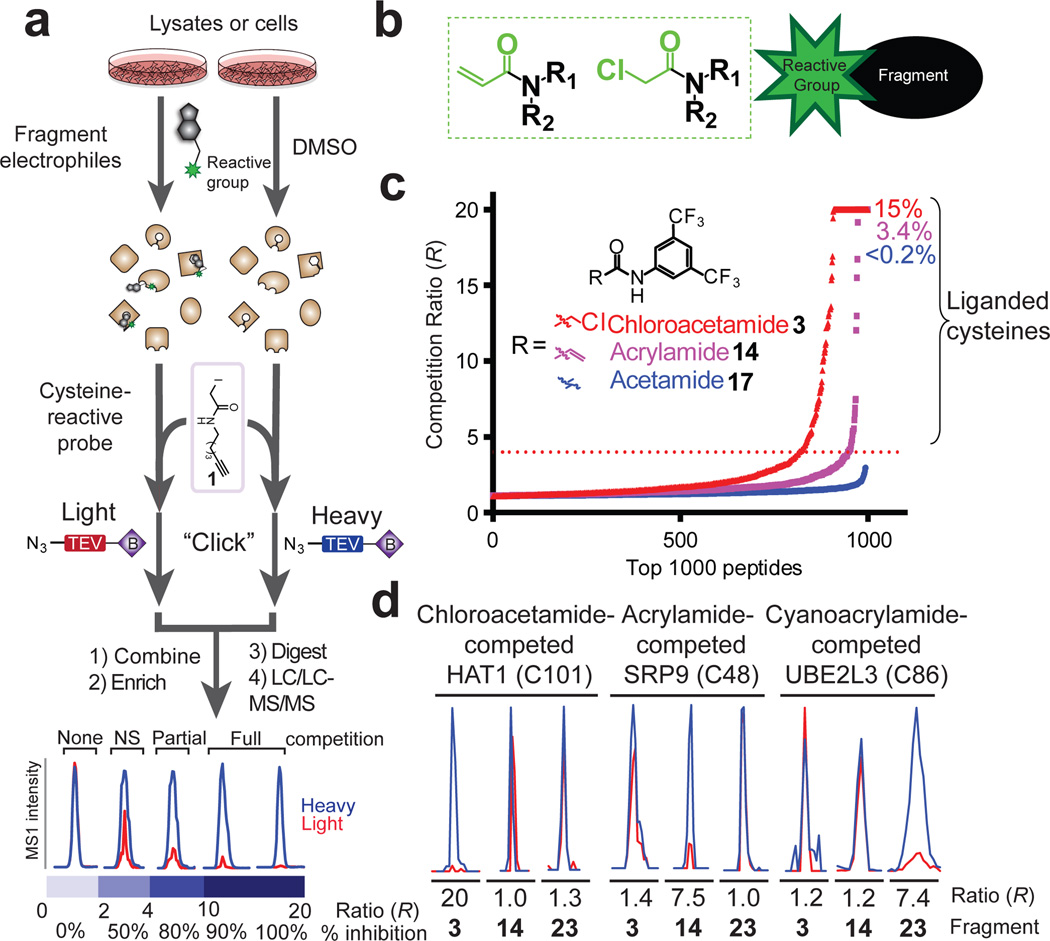
Figure 1. Proteome-wide screening of covalent fragments.
a, General protocol for competitive isoTOP-ABPP. Competition ratios, or R values, are measured by dividing the MS1 ion peaks for IA-alkyne (1)-labeled peptides in DMSO-treated (heavy, or blue) versus fragment-treated (light, or red) samples. b, General structure of electrophilic fragment library, where the reactive (electrophilic) and binding groups are colored green and black, respectively. c, Competitive isoTOP-ABPP analysis of the MDA-MB-231 cell proteome pre-treated with the electrophilic 3,5-di(trifluoromethyl)aniline chloroacetamide 3 and acrylamide 14 fragments, along with the non-electrophilic acetamide analogue 17 (500 µM each). Proteomic reactivity values, or liganded cysteine rates, for fragments were calculated as the percentage of total cysteines with R values ≥ 4 in DMSO/fragment (heavy/light) comparisons. d, Representative MS1 peptide ion chromatograms from competitive isoTOP-ABPP experiments marking liganded cysteines selectively targeted by one of three fragments 3, 4, and 23.