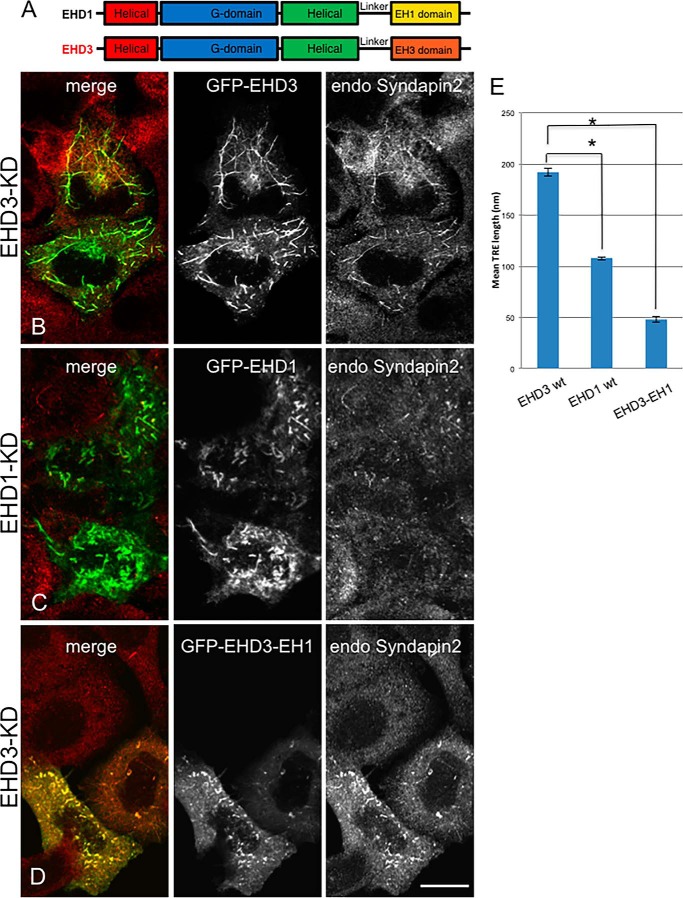
FIGURE 3.
The EH domain is responsible for the differential function of EHD1 and EHD3 in vesiculation and TRE stabilization, respectively. A, the C-terminal EHD proteins EHD1 and EHD3 share 86% identity and have a conserved domain architecture comprised of four domains: two helical domains, a G domain, and a C-terminal EH domain. B—D, HeLa cells were treated with EHD3 siRNA (B and D) or EHD1 siRNA (C) for 48 h. Cells were then transfected with (B) siRNA-resistant GFP-myc-EHD3 (WT), (C) siRNA-resistant GFP-myc-EHD1 (WT), and (D) siRNA-resistant GFP-myc-EHD3-EH1. TRE morphology was assessed by immunostaining with endogenous Syndapin2. Note that untransfected cells in C and D lack TRE. E, quantitative analysis of mean TRE length was measured in 100 cells from three independent experiments as in B–D. Significance was assessed by analysis of variance.*, p < 0.01. Scale bar = 10 μm.