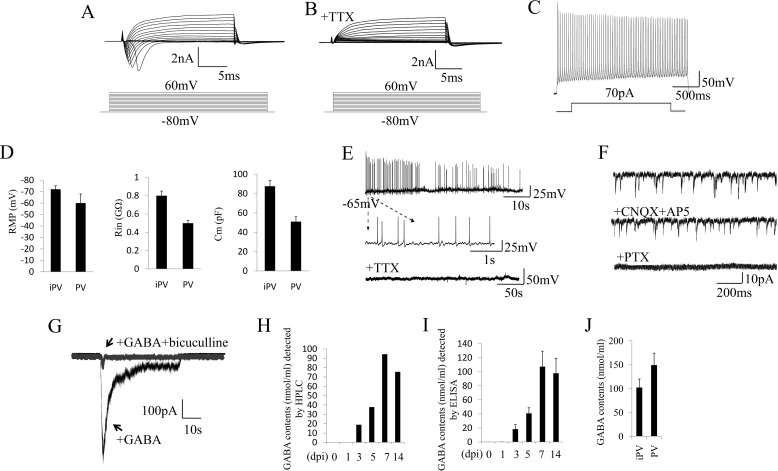
FIGURE 4.
Electrophysiological properties of iPV neurons. A, representative traces of whole-cell currents in voltage-clamp mode at 7 days post infection. B, TTX could abolish the sodium currents. C, action potentials evoked by step-depolarization of the membrane in current-clamp mode at 7 days post infection. D, analysis of membrane properties including resting membrane potential (RMP), membrane input resistances (Rin), and membrane capacitance (Cm) in iPV neuron and endogenous PV neuron. MΩ, megaohms; pF, picofarads. E, iN cells show spontaneous action potentials, which could be inhibited by the application of TTX. F, iN cell spontaneous PSCs could not be reduced by CNQX+AP5 but could be abolished by PTX. G, GABA-evoked PSCs could be blocked by bicuculline. H and I, HPLC and ELISA detection demonstrate that GABA was released by induced PV neurons in the culture medium with a peak at 7 dpi. J, GABA level in iPV neuron and endogenous PV neuron.