FIGURE 1.
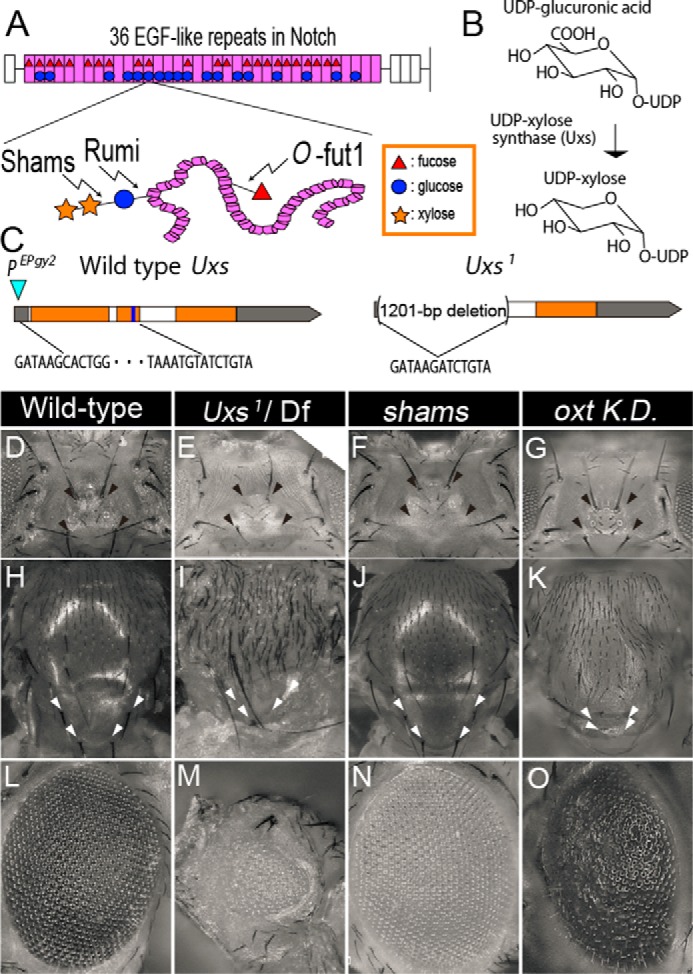
Overlaps in the Uxs-mutant, shams-mutant, and oxt knockdown phenotypes. A, upper: schematic of the EGF-like repeats in Notch, showing the O-glucose trisaccharide and monosaccharide O-fucose. The extracellular domain of Drosophila Notch has 36 EGF-like repeats (pink); 23 can be O-fucosylated (red triangles) and 18 can be O-glucosylated (blue circles). Lower: O-fucose (red triangle) is added by O-fut1. During the synthesis of the O-glucose trisaccharide (O-glucose-xylose-xylose), the O-glucose (blue circle) and first xylose (yellow star) are added by Rumi and Shams, respectively. B, schematic of UDP-xylose biosynthesis. Uxs is an essential enzyme for the de novo synthesis of UDP-xylose in Drosophila. C, genomic organization of the Drosophila Uxs locus, showing the untranslated (gray) and protein-coding (orange) regions of the Uxs gene exon, introns (white), and the region encoding a nucleotide-binding site (blue). A P-element (EPgy2) insertion site is indicated by a blue triangle. The 1201-bp deletion in Uxs1 is indicated by parentheses; the end points are shown by the DNA sequence. D-O, phenotypes of the head (D–G), notum (H–K), and eye (L–O) of wild-type (D, H, and L), and Uxs1/Df(3L)Exel6112 (E, I, and M) and shams34 homozygotes (F, J, and N), and oxt knockdown flies (G, K, and O). Missing ocellar and post-vertical bristles are indicated by black (D–G) and white (H–K) arrowheads, respectively. sca-Gal4 (G), ap-Gal4 (K), or GMR-Gal4 (O) were used for the oxt knockdown.
