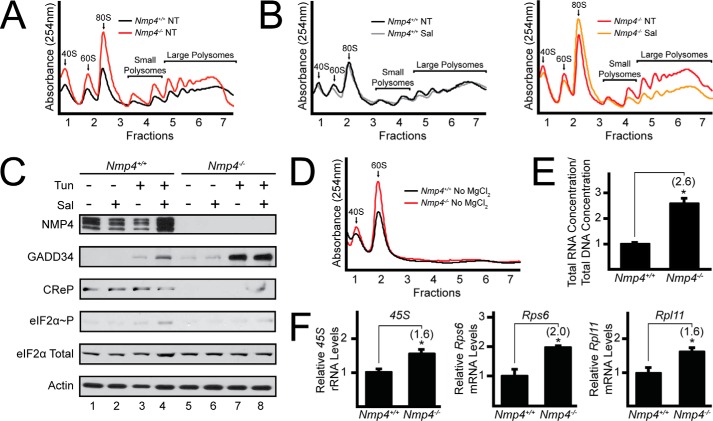
FIGURE 2.
Deletion of Nmp4 in MSPCs increases ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. A, lysates were collected from WT and Nmp4−/− MSPCs, and equal amounts of total RNA were layered on top of 10–50% sucrose gradients followed by ultracentrifugation and analysis of whole-lysate polysome profiles at 254 nm. B, polysome profiles were conducted as in panel A with the addition of treatment of WT and Nmp4−/− cells with salubrinal for 6 h or no treatment (NT). C, WT and Nmp4−/− MSPCs were treated individually or in combination with salubrinal and tunicamycin for 6 h as indicated, and the indicated proteins were measured by immunoblot. Quantification of eIF2α∼P was conducted using ImageJ software. Values feature the lane number in the immunoblot, with the first lane on the left designated as lane 1, followed by quantification of eIF2α-P in parentheses: 1(1); 2(1); 3(1.6); 4(3.3); 5(0.6); 6(0.8); 7(1.3); 8(2.4). D, levels of 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits were measured as in panel A with the exception that MgCl2 was omitted in the lysis and sucrose gradients. E, total DNA and total RNA lysates were quantified from WT and Nmp4−/− MSPCs. F, the 45S rRNA and Rps6 and Rpl11 mRNAs were measured by qRT-PCR in WT and Nmp4−/− MSPCs. Panels A, B, C, and D are representative of three independent biological experiments. Relative values of three biological replicates are represented as histograms with the S.D. indicated for panels E and F. Differences between treatment groups are indicated by *.