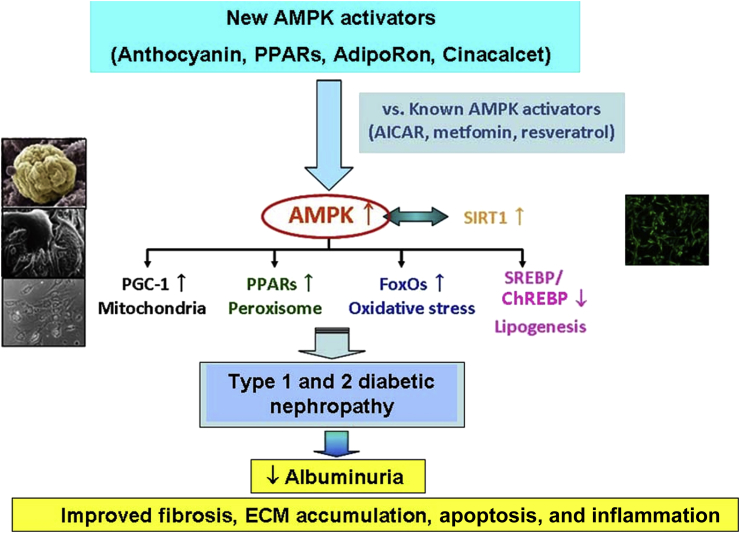
Figure 3.
Proposed renoprotective mechanisms in diabetic nephropathy by known and novel AMPK activators. Treatment with AMPK activators reduces albuminuria, glomerulosclerosis, and tubulointerstitial fibrosis in types 1 and 2 diabetic nephropathy by exerting effects on mitochondrial biogenesis, peroxisomal β-oxidation, oxidative stress, and lipogenesis through the activation of AMPK-SIRT1 signaling.
AICAR, 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside; AMPK, 5′ adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase; ChREBP, carbohydrate regulatory element–binding protein; ECM, extracellular matrix; FoxOs, forkhead transcription factors; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator--activated receptorγ coactivator 1α; PPARs, peroxisome proliferator–activated receptors; SIRT1, silent information regulator T1; SREBP, sterol regulatory element–binding protein.