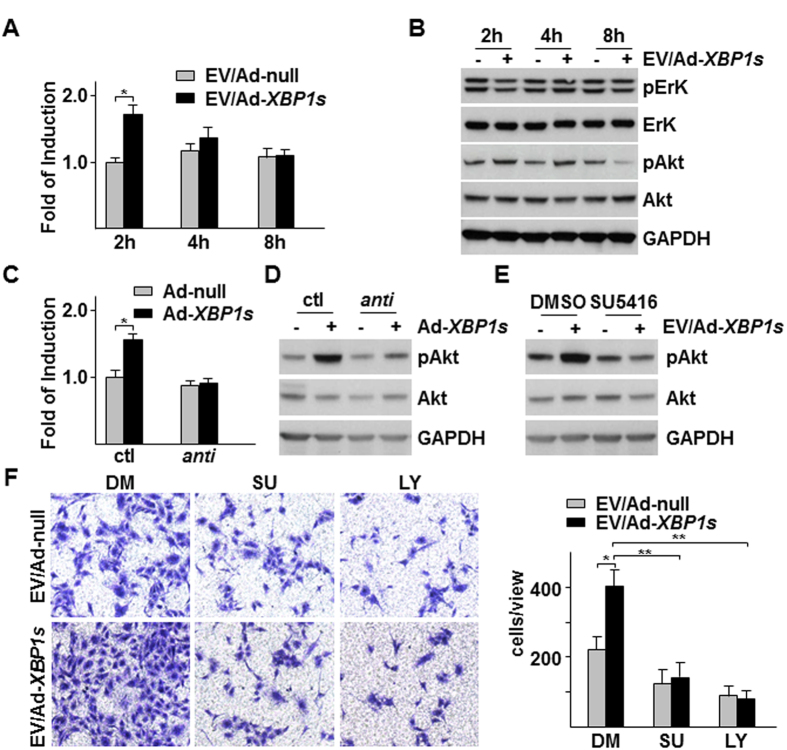
Figure 6. VEGF-PI3K/Akt pathway was responsible for Ad-XBP1s/HSMC-derived EVs-mediated EC migration.
(A,B) Ad-XBP1s/HSMC-derived EVs increased VEGF-A mRNA and Akt phosphorylation in HUVECs. EVs were isolated from Ad-XBP1s/HSMC condition medium (CM), reconstituted in M199 medium supplemented with 5 μg/ml insulin and 5 μg/ml transferrin and applied to HUVECs for time indicated, followed by quantitative RT-PCR analysis of VEGF-A mRNA (A) or western blot analysis of ErK and Akt (S473) phosphorylation (B). (C,D) Anti-miR-150 abolished XBP1s/HSMC-derived EVs-mediated VEGF-A expression and Akt. EVs were isolated from control (ctl) or anti-miR-150 transfected with Ad-XBP1s-infected HSMCs CM, reconstituted and applied to HUVECs for 2 h, followed by VEGF-A mRNA (C) and Akt (S473) phosphorylation assays (D). (E) SU5416 ablated Ad-XBP1s/HSMC-derived EVs-induced Akt phosphorylation. HUVECs were treated with EVs isolated from Ad-XBP1s in the presence of 10 μM SU5416 for 2 h, followed by Akt phosphorylation assay. (F) SU5416 and LY294002 attenuated Ad-XBP1s/HSMC-derived EVs-induced HUVEC migration. Transwell migration assays were performed with EVs isolated from Ad-XBP1s-infected HSMC CM in M199 medium supplemented with insulin and transferrin in the presence of SU5416 (SU) or 10 10 μM LY294002 (LY) for 8 h. Left panel shows the representative images of migrated cells while right panel shows average migrated cells per 10x view. Ad-null and DMSO (DM) were included as control. Data presented are representative images or mean of three independent experiments. (mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ANOVA, Dunnett post-test).