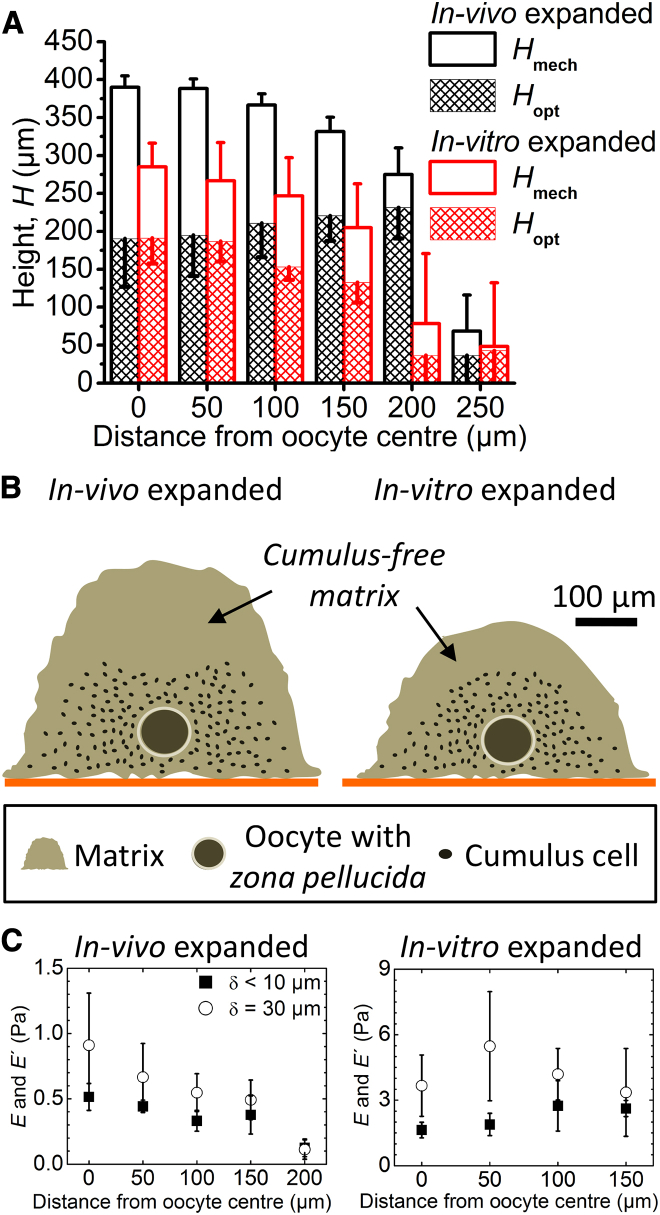
Figure 4.
Determination of COC dimensions. (A) Heights, Hmech (determined mechanically from the contact point) and Hopt (determined optically from the location of the topmost cumulus cells), as a function of the distance from the oocyte center. Data represent the mean and standard deviations from measurements on three COCs; error bars are drawn along one direction only to facilitate visualization. (B) Illustration of the approximate dimensions of the COC matrix and the location of cumulus cells within it, as determined from the spatial mapping of Hmech and Hopt. The height of the oocyte above the substrate was determined optically. Oocyte and cumulus cell sizes are drawn to scale. (C) Elasticity of COCs expanded in vivo (left) and in vitro (right) as a function of distance from the oocyte center. Young’s moduli in the linear elastic regime (solid squares) were determined through a fit with Eq. 1 for δ < 10 μm; elastic moduli at δ = 30 μm (open circles) were calculated with Eq. 2. Data represent the mean ± standard deviation from measurements on three individual COCs, except at 200 μm where only two of three in vivo expanded COCs had a matrix and were analyzed. To see this figure in color, go online.