Figure 9.
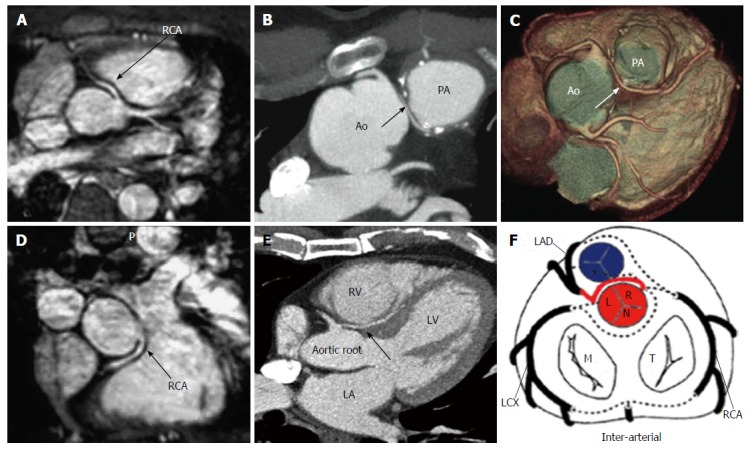
Example of interarterial course. A and D: Anomalous origin of the right coronary artery from the left sinus of Valsalva with an interarterial course between the aorta and the pulmonary artery (arrow)[19]; B and C: Interarterial coronary artery in a 56-year-old man with chest pain. CT image (B) and volume-rendered image (C) show an interarterial LAD artery (arrow) arising from the RCA and coursing between the aorta (Ao) and pulmonary artery (PA). Note the short-segment narrowing of the proximal LAD artery, a finding likely related to the patient’s anomalous anatomy[14,15]; E: CT image, venous phase, three chamber view shows interarterial course of the left coronary artery between the aortic root and the right ventricular outflow tract (black arrow). RV: Right ventricle; LA: Left atrium; LV: Left ventricle; F: Schematic representation of interarterial course; LAD: Left anterior descending; LCX: Left circumflex; RCA: Right coronary artery; M: Mitral valve; T: Tricuspid valve; L: Left sinus of Valsalva; R: Right sinus of Valsalva; N: Non-coronary sinus.
