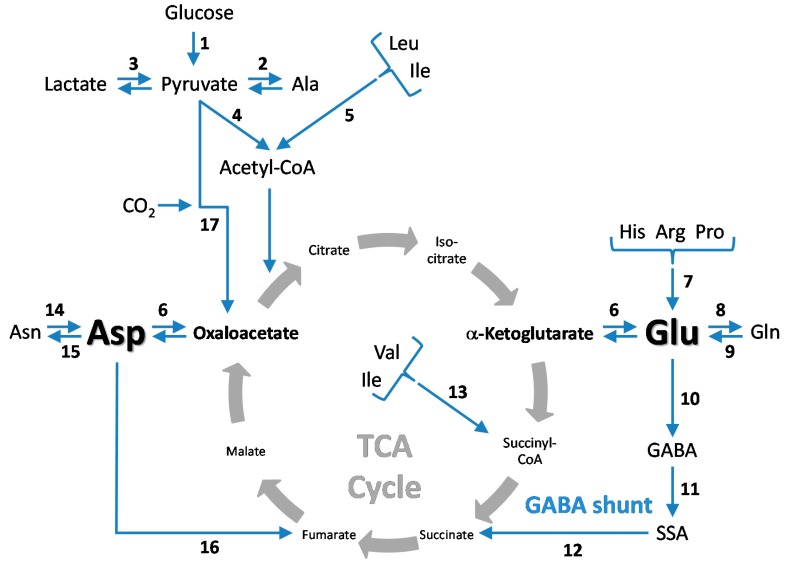
Figure 3.
One-compartment model highlighting the central role of glutamate as a buffer of C4/C5 intermediates in the brain. The diagram shows the standard depictions of the TCA cycle and GABA shunt in the brain. In addition the diagram indicates how glutamate acts as a buffer for C5 intermediates (α-ketoglutarate, glutamine) and C4 intermediates (GABA, succinic semialdehyde (SSA), succinate, fumarate, oxaloacetate, aspartate, and asparagine). Key enzymes/metabolic pathways: 1, Aerobic glycolysis; 2, alanine aminotransferase; 3, lactate dehydrogenase; 4, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; 5, metabolism of leucine and isoleucine (in part) to acetyl-CoA; 6, aspartate aminotransferase; 7, metabolism of histidine, arginine and proline resulting in the incorporation of 5-carbon units into glutamate; 8, glutamine synthetase; 9, glutaminase; 10, glutamate decarboxylase; 11, GABA aminotransferase; 12, succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase; 13, anaplerotic metabolism of isoleucine (in part) and valine to succinyl-CoA; 14, asparagine synthetase; 15, asparaginase; 16, enzymes of the purine nucleotide cycle; 17, anaplerotic pyruvate carboxylase. Note that the pentose phosphate pathway is present in brain but is not included in this diagram. Also not shown are all the reaction intermediates and cofactors.