Figure 4.
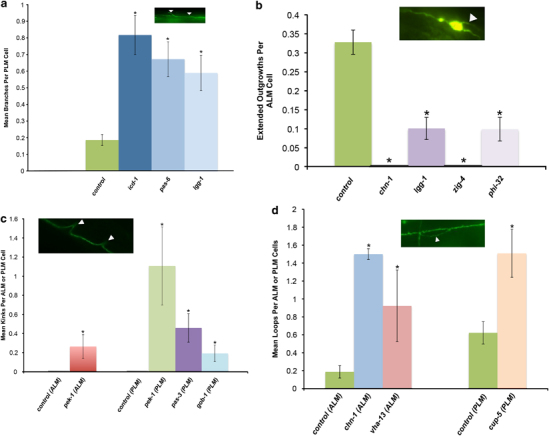
Effects of neuron-targeted RNAi knockdown of proteostasis components on the neuronal morphology of naturally aged touch receptor neurons. Pmec-4GFP animals were treated with RNAi for the corresponding gene starting at the late L4 stage and morphological changes, either branches (a) extended outgrowths (b), kinks (c) or loops (d) were quantified on day 5 of adulthood. Data were analyzed using the Mann–Whitney U-test with Holm–Sidak step-down comparisons. Branches: N=120, 131, 107, 242 neurons for icd-1, pas-6, lgg-1 and empty vector control, respectively. Branches: P⩽0.004 for each gene versus the corresponding control. Extended outgrowths: N=96, 109, 38, 91, 268 neurons for chn-1, lgg-1, zig-4, phi-32 and empty vector control, respectively. Extended outgrowths: P⩽0.011 for each gene versus the corresponding control. Kinks: N=52, 48, 53, 56 and 172 neurons for gob-1, pas-3, pek-1 (ALM), pek-1(PLM) and empty vector control, respectively. Kinks: P<0.01 for each gene versus the corresponding control. Loops: N=96, 26, 55 and ⩾172 for chn-1(ALM), vha-13(ALM), cup-5(PLM) and empty vector control, respectively. Loops: P<0.04 for each gene versus the corresponding control. GFP, green fluorescent protein; RNAi, RNA interference.
