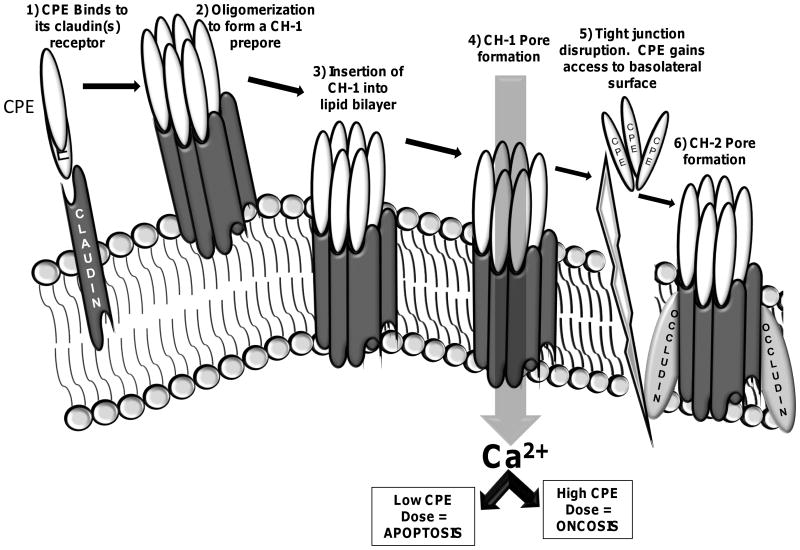
Figure 5.
Current model for the mechanism of action of CPE. CPE binds to claudin receptors to form small complexes. Those small complexes then oligomerize on the host cell surface to form an ∼450 kDa prepore known as CH-1. The prepore inserts into the membrane to form an active pore that alters host plasma membrane permeability for small molecules. As a result, calcium enters the cytoplasm and triggers either apoptosis (caused by low CPE doses, where there is a modest calcium influx) or oncosis (caused by high CPE doses, where there is a strong calcium influx). Reproduced with permission from (1).