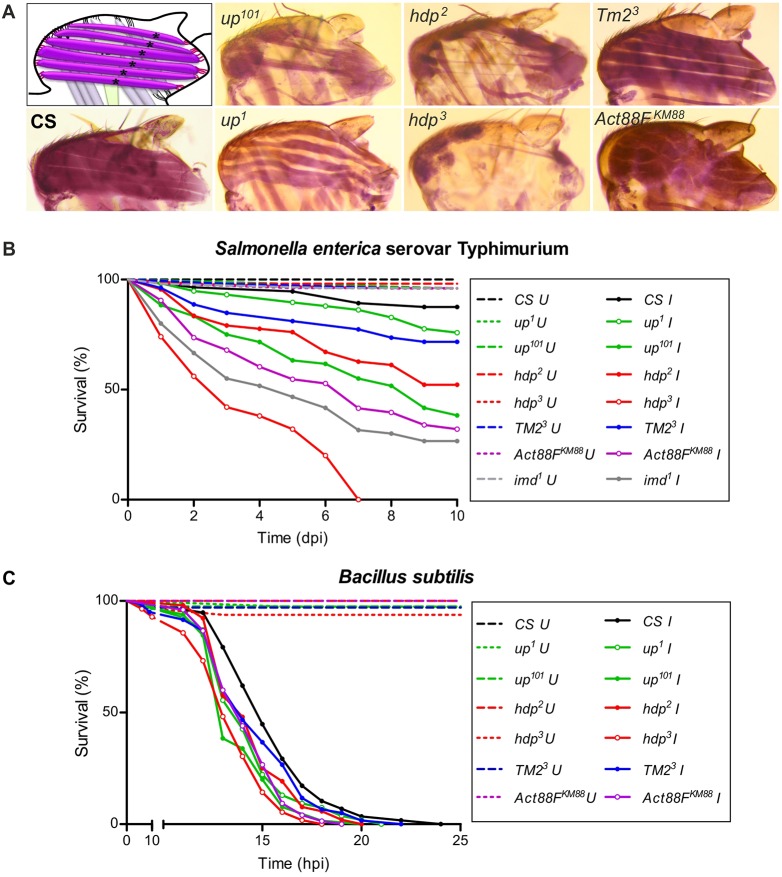
Fig. 1.
IFM mutants are susceptible to bacterial infection. (A) Hematoxylin-stained hemithoraces of the fly strains used in the study, alongside a representative schematic, show a spectrum of defects in the IFMs. CS: the wild-type fly strain Canton-S. (B,C) Survival curves of the muscle mutants post-infection with (B) Salmonella and (C) Bacillus subtilis by septic injury. A log-rank test was done for estimating the significance of the survival curves. (B) Salmonella infected versus uninfected: Canton-S, P=0.0094; up1, P=0.0034; up101, P<0.0001; hdp2, P<0.0001; hdp3, P<0.0001; TM23, P=0.0006; Act88FKM88, P<0.0001. Mutant versus wild type: up1, P=0.1171; up101, P<0.0001; hdp2, P<0.0001; hdp3, P<0.0001; TM23, P=0.0364; Act88FKM88, P<0.0001. (C) Bacillus infected versus uninfected: All fly strains, P<0.0001. Mutant versus wild type: up1, P=0.0139; up101, P=0.0002; hdp2, P=0.0346; hdp3, <0.0001; TM23, P=0.1646; Act88FKM88, P=0.0009. n>80. Open circles, IFM-specific mutants; dashed lines, uninfected controls; U, uninfected; I, infected; dpi, days post-infection; hpi, hours post-infection.