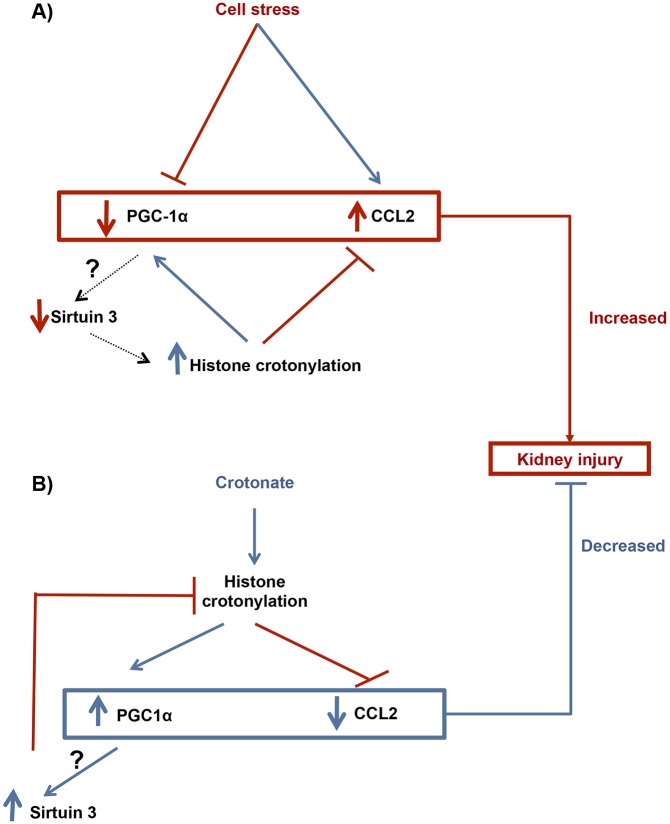
Fig. 8.
Working hypothesis of histone lysine crotonylation in kidney injury. (A) Kidney cell stressors. Cell stressors, such as TWEAK, decrease PGC-1α and increase CCL2 expression. These changes might contribute to tissue injury. We hypothesize that the decreased PGC-1α expression might contribute to decreased expression of the crotonylase SIRT3 and, this, in turn, limits the decrease in PGC-1α and SIRT3 expression by promoting histone crotonylation at the PGC-1α and SIRT3 genes, as observed in cultured cells. (B) Therapeutic response to crotonate. Crotonate increased overall histone crotonylation and increased the expression of PGC-1α and SIRT3, and decreased CCL2 expression. We hypothesize that these changes might contribute to the observed nephroprotection afforded by crotonate. The increased SIRT3 expression could, in turn, limit histone crotonylation as a negative-feedback mechanism.