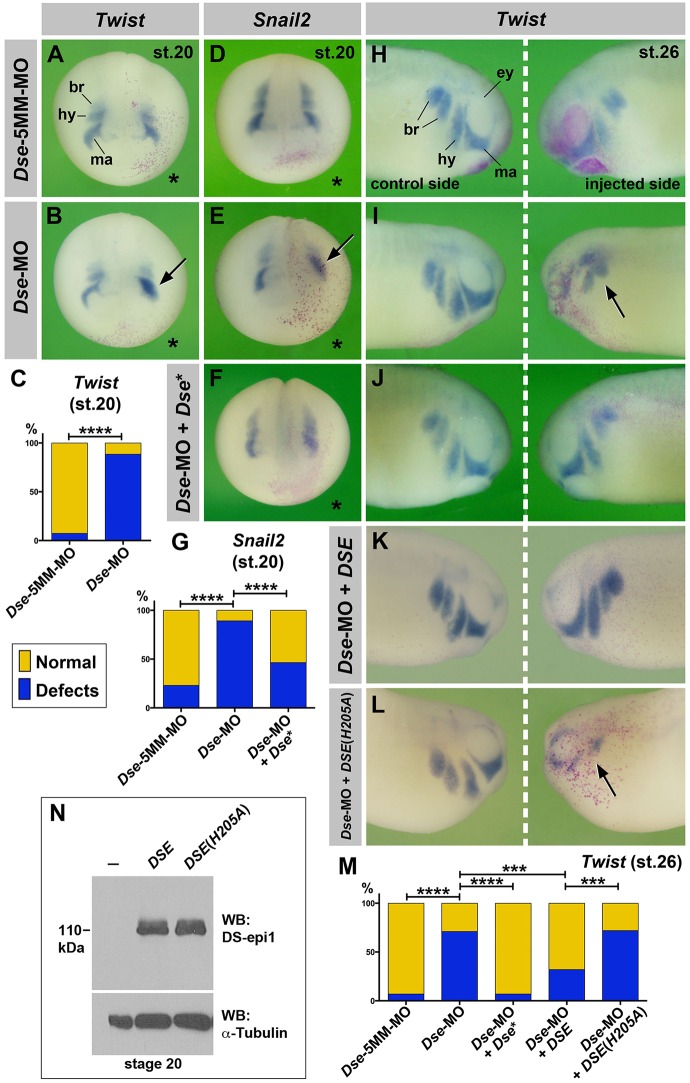
Fig. 5.
DS-epi1 regulates CNC cell migration. (A-G) Anterior view of late neurula embryos. The injected side is marked with a star. Dse-MO impairs the segregation of Twist+ and Snail2+ CNC cells (arrows). The effect is reversed by 250 pg Dse* mRNA. A quantification of the percentage of embryos with defects is shown in C and G. (H-M) Lateral view of tailbud embryos. Dse-MO leads to defective migration of Twist+ CNC cells (arrow) on the injected side, which is rescued by the co-injection of 250 pg Dse* mRNA and 25 pg pcDNA3/CTAP-DSE plasmid, but not 25 pg pcDNA3/CTAP-DSE (H205A) plasmid DNA. A quantification of the percentage of embryos with defects is shown in M. (N) Western blot analysis of lysates from embryos injected with 100 pg pcDNA3/CTAP-DSE or pcDNA3/CTAP-DSE (H205A) plasmid DNA and probed for DS-epi1. α-tubulin is a loading control. br, branchial segment; ey, eye; hy, hyoid segment; ma, mandibular segment. The proportion of examined embryos with the indicated phenotype was as follows: A, 15/16; B, 30/34; D, 41/46; E, 50/65; F, 20/37; H, 25/27; I, 31/41; J, 36/44; K, 27/40; and L, 14/18. ***P<0.005; ****P<0.0001 (Fisher's exact test with two-tailed P-value calculation).