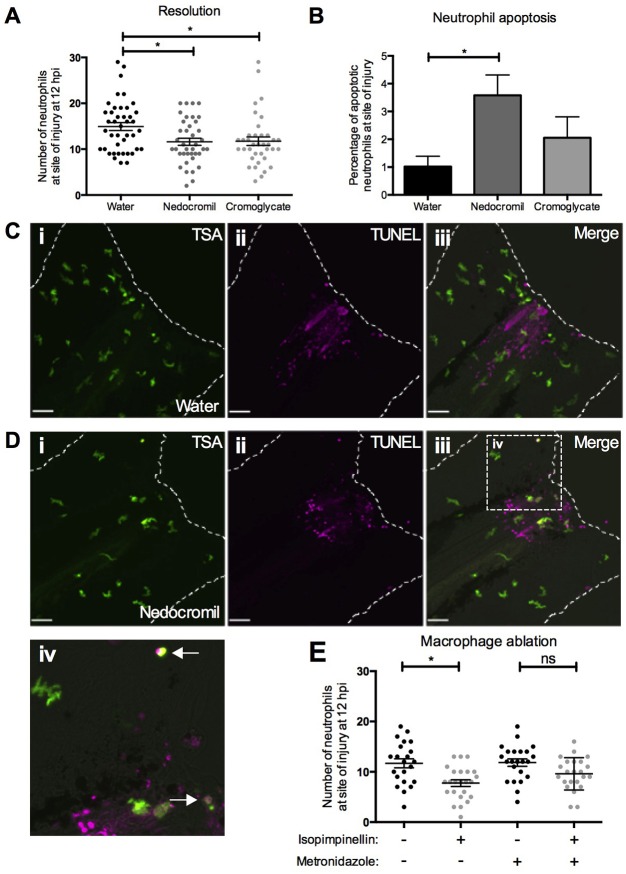
Fig. 6.
Clinical cromones promote neutrophil apoptosis to drive inflammation resolution in vivo. (A) Inflammation-resolution assay in mpx:GFP larvae injected with 0.4 pg/μl nedocromil or 0.5 pg/μl disodium cromoglycate at 6 hpi. Both compounds significantly reduce neutrophil numbers at the wound at 12 hpi compared to the water control (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple-comparison post-test; *P<0.5; n>36, performed as four independent experiments). (B-D) TUNEL assay in mpx:GFP larvae injected with water, 0.4 pg/μl nedocromil or 0.5 pg/μl disodium cromoglycate from 6 hpi and fixed at 12 hpi. Numbers of TSA-positive neutrophils and TSA/TUNEL double-positive apoptotic neutrophils at the site of injury were measured to calculate percentage neutrophil apoptosis, which was increased in nedocromil-treated larvae (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple-comparison post-test; *P<0.05; n>54, performed as three independent experiments). (C,D) Illustrative images of water-injected (C) and nedocromil-injected (D) larvae following TSA/TUNEL staining (scale bars: 40 μm). Broken lines indicate the outline of the tail-fin. White arrows in magnified view of boxed area in Diii (Div) indicate apoptotic neutrophils, identified by morphology and double TSA/TUNEL labelling. (E) Inflammation-resolution assay in the absence of macrophages. Metronidazole ablation of macrophages impairs the effect of isopimpinellin (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple-comparison post-test to compare selected columns; *P<0.05; ns, non-significant; n>20; performed as three independent experiments).