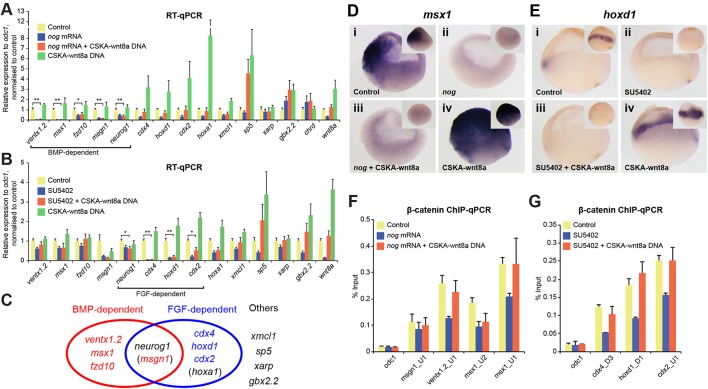
Fig. 5.
BMP or FGF signalling is required for wnt8a target gene expression but not for β-catenin recruitment. (A) BMP signalling is required for context-specific transcriptional regulation by Wnt8a signalling, but only of some wnt8a target genes. Two- to four-cell stage embryos were injected with BMP antagonist noggin (nog) mRNA. CSKA-wnt8a DNA was injected additionally to reinstate Wnt8a expression (as endogenous wnt8a expression is itself regulated by BMP signalling). Expression was analysed by RT-qPCR at the early gastrula stage. When BMP signalling is blocked, expression of BMP-dependent genes remains reduced even when Wnt8a expression is reinstated. (B) FGF signalling is required for context-specific transcriptional regulation by Wnt8a signalling, but only of some wnt8a target genes. Embryos were treated with the FGFR inhibitor SU5402 from the 1000/2000-cell stage through the early gastrula and injected where indicated with CSKA-wnt8a DNA at the two- to four-cell stages (to reinstate Wnt8a expression, as endogenous wnt8a expression is itself regulated by FGF signalling). When FGF signalling is inhibited, expression of FGF-dependent genes remains reduced, even when Wnt8a expression is reinstated. (C) wnt8a targets can therefore be classified into BMP-dependent or FGF-dependent genes. Note that some genes belong to both groups and others are neither BMP nor FGF dependent. (D,E) In situ hybridisation shows expression of msx1 (D) and hoxd1 (E) in sagittal sections and lateral views (insets) of control uninjected and experimentally manipulated embryos as indicated (dorsal to the right). (F) BMP signalling is not required for wnt8a-regulated β-catenin recruitment to BMP-dependent wnt8a target gene loci. Embryos were treated as in A and analysed by β-catenin ChIP-qPCR at the early gastrula stage. (G) FGF signalling is not essential for wnt8a-regulated β-catenin recruitment to FGF-dependent wnt8a target gene loci. Embryos were treated as in B and analysed by β-catenin ChIP-qPCR at the early gastrula stage. Uninjected, untreated embryos were used as controls in A,B,D-G. *P<0.1, **P<0.05; two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bars represent s.d. of four biological replicates (A,B) or s.e.m. of three biological replicates (F,G). Note that wnt8a gene expression itself was decreased by BMP or FGF pathway inhibition (wnt8a blue bars in A,B) but restored by co-injection of CSKA-wnt8a DNA (wnt8a orange bars in A,B) compared with controls (wnt8a yellow bars in A,B), and that higher wnt8a expression levels with CSKA-wnt8a DNA (wnt8a green bars in A,B) reflect both expression of endogenous wnt8a and expression from CSKA-wnt8a DNA, resulting in upregulation of several wnt8a target genes (in A,B).