Fig. 1.
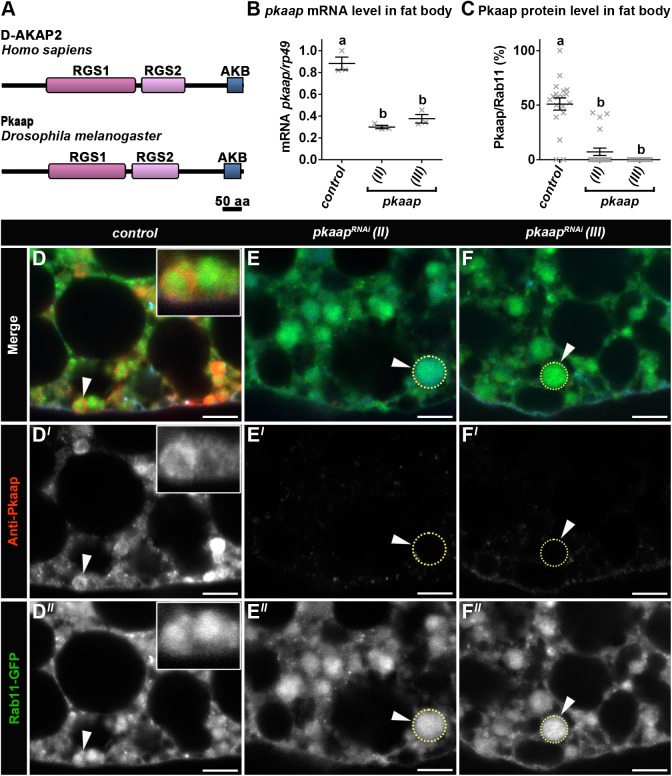
Expression of CG-GAL4>UAS-pkaap in fat body tissue. (A) A schematic diagram showing the domain structure of D-AKAP2 and Pkaap proteins. D-AKAP2 and Pkaap proteins contain regulator of G protein signalling (RGS) domains and PKA-binding (AKB) domain. (B) The expression of pkaap mRNA was characterised by quantitative real-time PCR in fat body tissue from the following genotypes: control, pkaapRNAi chromosome II and pkaapRNAi chromosome III. mRNA levels were normalised against rp49 mRNA levels. Three independent sets of samples were analysed from late third larval instar (−4 h puparium formation). One-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison test showed significant differences between the means for the genotypes (depicted by different letters on the bars, P<0.0001). Data presented as mean±s.e.m. (C) Percentage of Pkaap colocation with Rab11 vesicles in the fat body cells from the following genotypes: control, pkaapRNAi chromosome II and pkaapRNAi chromosome III. One-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison test showed significant differences between the means for the genotypes (depicted by different letters on the bars, P<0.0001). (D-F) Confocal micrographs showing localisation of Pkaap detected with an anti-Pkaap antibody (red in D-F; greyscale in D′-F′) in relation to Rab11-GFP vesicles (green in D-F; greyscale in D″-F″) in (D) control, (E) pkaapRNAi chromosome II and (F) pkaapRNAi chromosome III fat bodies. The plasma membrane was detected with Alexa Fluor® 568 Phalloidin (cyan in D-F). Data is representative of at least ten independent replicates. Scale bar: 5 μm.