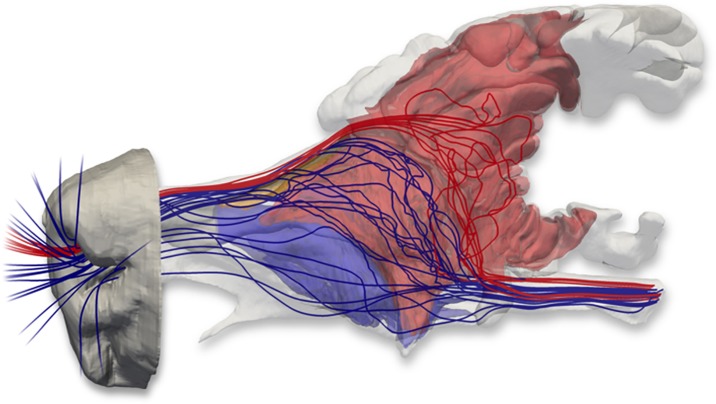
Fig. 7.
Nasal airflow patterns in the bobcat obtained from a CFD simulation of airflow in the nose. The fronto-ethmoturbinals (red) and maxilloturbinals (blue) were segmented from the MRI data and are visualized with flow streamlines extracted from the CFD solution. As Craven et al. (2010) found in the domestic dog, separate respiratory and olfactory airflow paths exist in the nasal cavity of the bobcat. Olfactory airflow (illustrated by red streamlines) reaches the olfactory recess via the dorsal meatus, bypassing the convoluted maxilloturbinals. Respiratory airflow (illustrated by blue streamlines) is directed away from the olfactory recess and toward the internal nares by the maxilloturbinals and the anterior extensions of the fronto-ethmoturbinals.