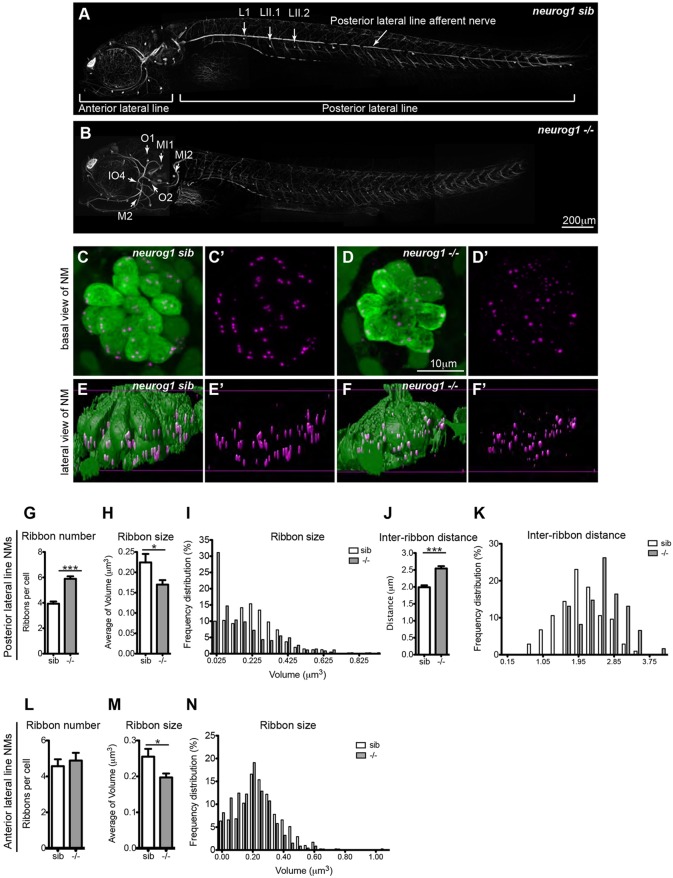
Fig. 2.
Innervation is required for regulation of ribbon size, number and localization. (A,B) Afferent innervation in neurogenin (neurog1) siblings (sib) (A) and mutants (–/–) (B) as detected by antibody staining for acetylated tubulin. neurog1 mutants (B) lack afferent and efferent (data not shown) innervation of posterior lateral line hair cells but not anterior lateral line hair cells. A total of nine neuromasts (NM) per condition were used for confocal microscopy imaging and ribbon analysis: three posterior lateral line neuromasts (L1, LII.1, LII2) and three anterior lateral line neuromasts (O2, MI1, MI2, IO4 or M2) per larvae were measured in three different larvae. (C–D′) Projections of confocal images of the posterior lateral line neuromasts immunolabeled to show hair cells (green, anti-parvalbumin antibody) and ribbons (magenta, anti-RibeyeB antibody). (E–F′) Lateral views of surface renderings of neuromasts in C–D′ generated by Huygens software. Ribbon size, number and inter-ribbon distance were obtained from the surface renderings of the neuromasts (see Materials and Methods). In neurog1 siblings, ribbons were found at the base of hair cells (E,E′), whereas in neurog1 mutants, ribbons were found both in the cytoplasm and at the base of posterior lateral line hair cells (F,F′). Additionally, in neurog1 mutants, ribbons were fewer in number (G), smaller in average size (H,I) and the distance between ribbons was also increased (J,K). The number of ribbons per cell in anterior lateral line hair cells, which are innervated, did not differ between neurog1 mutants and sibling larvae (L) but ribbon size was smaller in neurog1 mutant hair cells (M). Ribbon size and number were obtained from the surface renderings of the neuromasts (see Materials and Methods). *P=0.09 in H, *P=0.03 in M, ***P<0.0001. Statistical analysis of ribbons (unpaired two tailed t-test) was performed on averages of averages – we calculated the average of ribbons per cell in a given neuromast and then averaged this number across nine total neuromasts (three neuromasts in three different larvae). Posterior lateral line neuromasts in neurog1 mutants had an average of nine hair cells per neuromast, whereas anterior lateral line neuromasts had an average of 11 hair cells per neuromast. Posterior lateral line neuromasts in neurog1 siblings had an average of 12 hair cells per neuromast, whereas anterior lateral line neuromasts had an average of 10 hair cells per neuromast. Results are mean±s.e.m.