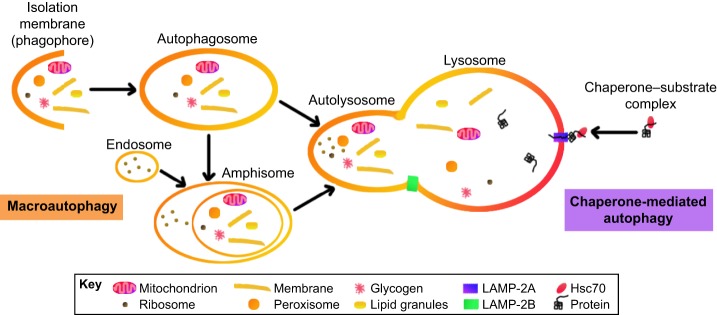
Fig. 3.
Mammalian pathways of macroautophagy and chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA). In macroautophagy, a variety of cargo can be engulfed by an autophagosome, which fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome to then degrade its contents. Alternatively, an autophagosome can fuse with an endosome to form an amphisome, which then fuses with the lysosome. The processes of autophagosome and amphisome fusion with the lysosome are thought to require LAMP-2B, although any direct binding partners of LAMP-2B, which are important for these processes, are unknown. In CMA, target proteins are recognized and bound by heat shock cognate protein 70 (Hsc70; also known as HSPA8), which forms a chaperone–substrate complex that is transported to the lysosome, where interaction with LAMP-2A transport the target protein across the lysosome membrane.