Figure 1.
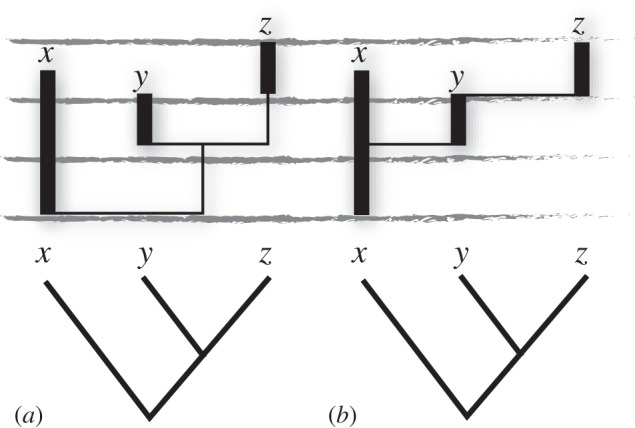
The relationship between cladograms, which consider only relative relationships, and phylogenies, which can represent absolute relationships. Both (a,b) are compatible with the same hypothesis of cladistic relationships; however, (b) represents a hypothesis of budding ancestry between (x,y), and anagenesis between (y,z). Phylogeny (a) implies gaps (represented by thin vertical lines subtending the thick vertical bars which reflect the stratigraphic ranges of taxa x–z) in the fossil record to accommodate the sister group relationship between lineages x and y + z, and between y and z. Meanwhile phylogeny (b) does not imply any gaps in the fossil record.
